The TLR4 antagonist Eritoran protects mice from lethal influenza infection
- PMID: 23636320
- PMCID: PMC3725830
- DOI: 10.1038/nature12118
The TLR4 antagonist Eritoran protects mice from lethal influenza infection
Abstract
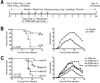
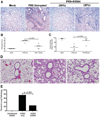
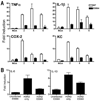
There is a pressing need to develop alternatives to annual influenza vaccines and antiviral agents licensed for mitigating influenza infection. Previous studies reported that acute lung injury caused by chemical or microbial insults is secondary to the generation of host-derived, oxidized phospholipid that potently stimulates Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)-dependent inflammation. Subsequently, we reported that Tlr4(-/-) mice are highly refractory to influenza-induced lethality, and proposed that therapeutic antagonism of TLR4 signalling would protect against influenza-induced acute lung injury. Here we report that therapeutic administration of Eritoran (also known as E5564)-a potent, well-tolerated, synthetic TLR4 antagonist-blocks influenza-induced lethality in mice, as well as lung pathology, clinical symptoms, cytokine and oxidized phospholipid expression, and decreases viral titres. CD14 and TLR2 are also required for Eritoran-mediated protection, and CD14 directly binds Eritoran and inhibits ligand binding to MD2. Thus, Eritoran blockade of TLR signalling represents a novel therapeutic approach for inflammation associated with influenza, and possibly other infections.
Figures
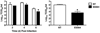
References
-
- Kalil AC, et al. Influence of severity of illness on the effects of eritoran tetrasodium (E5564) and on other therapies for severe sepsis. Shock. 2011;36:327–331. - PubMed
-
- Mullarkey M, et al. Inhibition of endotoxin response by E5564, a novel Toll-like receptor 4-directed endotoxin antagonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2003;304:1093–1102. - PubMed
-
- Thompson WW, et al. Mortality associated with influenza and respiratory syncytial virus in the United States. JAMA. 2003;289:179–186. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

