Dry eye modifies the thermal and menthol responses in rat corneal primary afferent cool cells
- PMID: 23636717
- PMCID: PMC3727064
- DOI: 10.1152/jn.00222.2013
Dry eye modifies the thermal and menthol responses in rat corneal primary afferent cool cells
Abstract
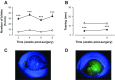
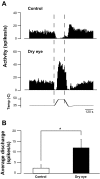
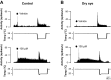
Dry eye syndrome is a painful condition caused by inadequate or altered tear film on the ocular surface. Primary afferent cool cells innervating the cornea regulate the ocular fluid status by increasing reflex tearing in response to evaporative cooling and hyperosmicity. It has been proposed that activation of corneal cool cells via a transient receptor potential melastatin 8 (TRPM8) channel agonist may represent a potential therapeutic intervention to treat dry eye. This study examined the effect of dry eye on the response properties of corneal cool cells and the ability of the TRPM8 agonist menthol to modify these properties. A unilateral dry eye condition was created in rats by removing the left lacrimal gland. Lacrimal gland removal reduced tears in the dry eye to 35% compared with the contralateral eye and increased the number of spontaneous blinks in the dry eye by over 300%. Extracellular single-unit recordings were performed 8-10 wk following surgery in the trigeminal ganglion of dry eye animals and age-matched controls. Responses of corneal cool cells to cooling were examined after the application of menthol (10 μM-1.0 mM) to the ocular surface. The peak frequency of discharge to cooling was higher and the cooling threshold was warmer in dry eye animals compared with controls. The dry condition also altered the neuronal sensitivity to menthol, causing desensitization to cold-evoked responses at concentrations that produced facilitation in control animals. The menthol-induced desensitization of corneal cool cells would likely result in reduced tearing, a deleterious effect in individuals with dry eye.
Keywords: cold cells; dry eye; rat; sensitization; trigeminal.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The role of corneal afferent neurons in regulating tears under normal and dry eye conditions.Exp Eye Res. 2013 Dec;117:79-87. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2013.08.011. Epub 2013 Aug 28. Exp Eye Res. 2013. PMID: 23994439 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dry eye sensitizes cool cells to capsaicin-induced changes in activity via TRPV1.J Neurophysiol. 2019 Jun 1;121(6):2191-2201. doi: 10.1152/jn.00126.2018. Epub 2019 Apr 10. J Neurophysiol. 2019. PMID: 30969886 Free PMC article.
-
Menthol activation of corneal cool cells induces TRPM8-mediated lacrimation but not nociceptive responses in rodents.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012 Oct 9;53(11):7034-42. doi: 10.1167/iovs.12-10025. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012. PMID: 22952122 Free PMC article.
-
Role of TRPM8 Channels in Altered Cold Sensitivity of Corneal Primary Sensory Neurons Induced by Axonal Damage.J Neurosci. 2019 Oct 9;39(41):8177-8192. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0654-19.2019. Epub 2019 Aug 30. J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31471469 Free PMC article.
-
The distinctive role of menthol in pain and analgesia: Mechanisms, practices, and advances.Front Mol Neurosci. 2022 Oct 5;15:1006908. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2022.1006908. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36277488 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Transient Receptor Potential Channels: Important Players in Ocular Pain and Dry Eye Disease.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Sep 2;14(9):1859. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14091859. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36145607 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Abnormal activity of corneal cold thermoreceptors underlies the unpleasant sensations in dry eye disease.Pain. 2016 Feb;157(2):399-417. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000000455. Pain. 2016. PMID: 26675826 Free PMC article.
-
The role of corneal afferent neurons in regulating tears under normal and dry eye conditions.Exp Eye Res. 2013 Dec;117:79-87. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2013.08.011. Epub 2013 Aug 28. Exp Eye Res. 2013. PMID: 23994439 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ocular Surface Ion-Channels Are Closely Related to Dry Eye: Key Research Focus on Innovative Drugs for Dry Eye.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Mar 3;9:830853. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.830853. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35308542 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dry eye sensitizes cool cells to capsaicin-induced changes in activity via TRPV1.J Neurophysiol. 2019 Jun 1;121(6):2191-2201. doi: 10.1152/jn.00126.2018. Epub 2019 Apr 10. J Neurophysiol. 2019. PMID: 30969886 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abe J, Hosokawa H, Sawada Y, Matsumura K, Kobayashi S. Ca2+-dependent PKC activation mediates menthol-induced desensitization of transient receptor potential M8. Neurosci Lett 397: 140–144, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Abelson MB, Ousler GW, 3rd, Maffei C. Dry eye in 2008. Curr Opin Ophthalmol 20: 282–286, 2009 - PubMed
-
- Acosta MC, Peral A, Luna C, Pintor J, Belmonte C, Gallar J. Tear secretion induced by selective stimulation of corneal and conjunctival sensory nerve fibers. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 45: 2333–2336, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Acosta MC, Tan ME, Belmonte C, Gallar J. Sensations evoked by selective mechanical, chemical, and thermal stimulation of the conjunctiva and cornea. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 42: 2063–2067, 2001b - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

