Inhibitory inputs tune the light response properties of dopaminergic amacrine cells in mouse retina
- PMID: 23636722
- PMCID: PMC3727066
- DOI: 10.1152/jn.00118.2013
Inhibitory inputs tune the light response properties of dopaminergic amacrine cells in mouse retina
Abstract
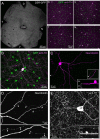
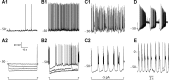
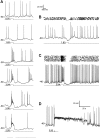
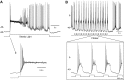
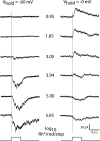
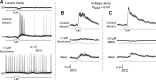
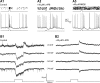
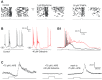
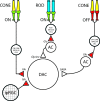
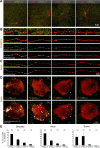
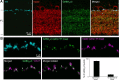
Dopamine (DA) is a neuromodulator that in the retina adjusts the circuitry for visual processing in dim and bright light conditions. It is synthesized and released from retinal interneurons called dopaminergic amacrine cells (DACs), whose basic physiology is not yet been fully characterized. To investigate their cellular and input properties as well as light responses, DACs were targeted for whole cell recording in isolated retina using two-photon fluorescence microscopy in a mouse line where the dopamine receptor 2 promoter drives green fluorescent protein (GFP) expression. Differences in membrane properties gave rise to cell-to-cell variation in the pattern of resting spontaneous spike activity ranging from silent to rhythmic to periodic burst discharge. All recorded DACs were light sensitive and generated responses that varied with intensity. The threshold response to light onset was a hyperpolarizing potential change initiated by rod photoreceptors that was blocked by strychnine, indicating a glycinergic amacrine input onto DACs at light onset. With increasing light intensity, the ON response acquired an excitatory component that grew to dominate the response to the strongest stimuli. Responses to bright light (photopic) stimuli also included an inhibitory OFF response mediated by GABAergic amacrine cells driven by the cone OFF pathway. DACs expressed GABA (GABA(A)α1 and GABA(A)α3) and glycine (α2) receptor clusters on soma, axon, and dendrites consistent with the light response being shaped by dual inhibitory inputs that may serve to tune spike discharge for optimal DA release.
Keywords: amacrine cell; dopaminergic neuron; electrophysiology; immunocytochemistry; retina.
Figures
References
-
- Alonso A, Llinas RR. Subthreshold Na+-dependent theta-like rhythmicity in stellate cells of entorhinal cortex layer II. Nature 342: 175–177, 1989 - PubMed
-
- Armstrong CM, Gilly WF. Access resistance and space clamp problems associated with whole-cell patch clamping. Methods Enzymol 207: 100–122, 1992 - PubMed
-
- Bloomfield SA, Dacheux RF. Rod vision: pathways and processing in the mammalian retina. Prog Retin Eye Res 20: 351–384, 2001 - PubMed
-
- Bunney BS, Grace AA. Acute and chronic haloperidol treatment: comparison of effects on nigral dopaminergic cell activity. Life Sci 23: 1715–1727, 1978 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

