Development and evaluation of a next-generation digital PCR diagnostic assay for ocular Chlamydia trachomatis infections
- PMID: 23637300
- PMCID: PMC3697714
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.00622-13
Development and evaluation of a next-generation digital PCR diagnostic assay for ocular Chlamydia trachomatis infections
Abstract
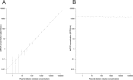
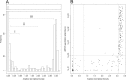
Droplet digital PCR (ddPCR) is an emulsion PCR process that performs absolute quantitation of nucleic acids. We developed a ddPCR assay for Chlamydia trachomatis infections and found it to be accurate and precise. Using PCR mixtures containing plasmids engineered to include the PCR target sequences, we were able to quantify with a dynamic range between 0.07 and 3,160 targets/μl (r(2) = 0.9927) with >95% confidence. Using 1,509 clinical conjunctival swab samples from a population in which trachoma is endemic in Guinea Bissau, we evaluated the specificity and sensitivity of the quantitative ddPCR assay in diagnosing ocular C. trachomatis infections by comparing the performances of ddPCR and the Roche Amplicor CT/NG test. We defined ddPCR tests as positive when we had ≥95% confidence in a nonzero estimate of target load. The sensitivity of ddPCR against Amplicor was 73.3% (95% confidence interval [CI], 67.9 to 78.7%), and specificity was 99.1% (95% CI, 98.6 to 99.6%). Negative and positive predictive values were 94.6% (95% CI, 93.4 to 95.8%) and 94.5% (95% CI, 91.3 to 97.7%), respectively. Based on Amplicor CT/NG testing, the estimated population prevalence of C. trachomatis ocular infection was ∼17.5%. Receiver-operator curve analysis was used to select critical cutoff values for use in clinical settings in which a balance between higher sensitivity and specificity is required. We concluded that ddPCR is an effective diagnostic technology suitable for both research and clinical use in diagnosing ocular C. trachomatis infections.
Figures

Comment in
-
Will droplet digital PCR become the test of choice for detecting and quantifying ocular Chlamydia trachomatis infection? Maybe not.Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2013 Nov;13(8):789-92. doi: 10.1586/14737159.2013.847792. Epub 2013 Oct 17. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2013. PMID: 24134626
Similar articles
-
Will droplet digital PCR become the test of choice for detecting and quantifying ocular Chlamydia trachomatis infection? Maybe not.Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2013 Nov;13(8):789-92. doi: 10.1586/14737159.2013.847792. Epub 2013 Oct 17. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2013. PMID: 24134626
-
Evaluation of a Chlamydia trachomatis-specific, commercial, real-time PCR for use with ocular swabs.Parasit Vectors. 2018 Feb 20;11(1):102. doi: 10.1186/s13071-018-2686-y. Parasit Vectors. 2018. PMID: 29463279 Free PMC article.
-
Risk factors for active trachoma and ocular Chlamydia trachomatis infection in treatment-naïve trachoma-hyperendemic communities of the Bijagós Archipelago, Guinea Bissau.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014 Jun 26;8(6):e2900. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0002900. eCollection 2014 Jun. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014. PMID: 24967629 Free PMC article.
-
Field evaluation of the Cepheid GeneXpert Chlamydia trachomatis assay for detection of infection in a trachoma endemic community in Tanzania.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2013 Jul 4;7(7):e2265. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0002265. Print 2013. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2013. PMID: 23861986 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced-cost Chlamydia trachomatis-specific multiplex real-time PCR diagnostic assay evaluated for ocular swabs and use by trachoma research programmes.J Microbiol Methods. 2017 Aug;139:95-102. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2017.04.010. Epub 2017 May 6. J Microbiol Methods. 2017. PMID: 28487054 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Detection of circulating Mycobacterium tuberculosis-specific DNA by droplet digital PCR for vaccine evaluation in challenged monkeys and TB diagnosis.Emerg Microbes Infect. 2018 Apr 24;7(1):78. doi: 10.1038/s41426-018-0076-3. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2018. PMID: 29691363 Free PMC article.
-
Four human Plasmodium species quantification using droplet digital PCR.PLoS One. 2017 Apr 19;12(4):e0175771. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0175771. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28423028 Free PMC article.
-
Chlamydia trachomatis-containing vacuole serves as deubiquitination platform to stabilize Mcl-1 and to interfere with host defense.Elife. 2017 Mar 28;6:e21465. doi: 10.7554/eLife.21465. Elife. 2017. PMID: 28347402 Free PMC article.
-
miRNAs that associate with conjunctival inflammation and ocular Chlamydia trachomatis infection do not predict progressive disease.Pathog Dis. 2017 Mar 1;75(2):ftx016. doi: 10.1093/femspd/ftx016. Pathog Dis. 2017. PMID: 28175294 Free PMC article.
-
Inverse relationship between microRNA-155 and -184 expression with increasing conjunctival inflammation during ocular Chlamydia trachomatis infection.BMC Infect Dis. 2016 Feb 3;16:60. doi: 10.1186/s12879-016-1367-8. BMC Infect Dis. 2016. PMID: 26842862 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO 2012. Global WHO alliance for the elimination of blinding trachoma by 2020. Wkly. Epidemiol. Rec. 87:161–168 - PubMed
-
- Burton MJ, Holland MJ, Makalo P, Aryee EAN, Alexander NDE, Sillah A, Faal H, West SK, Foster A, Johnson GJ, Mabey DCW, Bailey RL. 2005. Re-emergence of Chlamydia trachomatis infection after mass antibiotic treatment of a trachoma-endemic Gambian community: a longitudinal study. Lancet 365:1321–1328 - PubMed
-
- Chidambaram JD, Alemayehu W, Melese M, Lakew T, Yi E, House J, Cevallos V, Zhou Z, Maxey K, Lee DC, Shapiro BL, Srinivasan M, Porco T, Whitcher JP, Gaynor BD, Lietman TM. 2006. Effect of a single mass antibiotic distribution on the prevalence of infectious trachoma. JAMA 295:1142–1146 - PubMed
-
- Schachter J, West SK, Mabey D, Dawson CR, Bobo L, Bailey R, Vitale S, Quinn TC, Sheta A, Sallam S, Mkocha H, Faal H. 1999. Azithromycin in control of trachoma. Lancet 354:630–635 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

