The interaction of the cellular export adaptor protein Aly/REF with ICP27 contributes to the efficiency of herpes simplex virus 1 mRNA export
- PMID: 23637401
- PMCID: PMC3700301
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00738-13
The interaction of the cellular export adaptor protein Aly/REF with ICP27 contributes to the efficiency of herpes simplex virus 1 mRNA export
Abstract
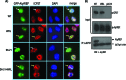
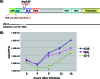
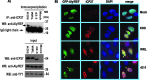
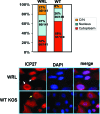
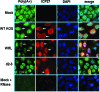
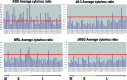
Herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1) protein ICP27 enables viral mRNA export by accessing the cellular mRNA export receptor TAP/NXF, which guides mRNA through the nuclear pore complex. ICP27 binds viral mRNAs and interacts with TAP/NXF, providing a link to the cellular mRNA export pathway. ICP27 also interacts with the mRNA export adaptor protein Aly/REF, which binds cellular mRNAs and also interacts with TAP/NXF. Studies using small interfering RNA (siRNA) knockdown indicated that Aly/REF is not required for cellular mRNA export, and similar knockdown studies during HSV-1 infection led us to conclude that Aly/REF may be dispensable for viral RNA export. Recently, the structural basis of the interaction of ICP27 with Aly/REF was elucidated at atomic resolution, and it was shown that three ICP27 residues, W105, R107, and L108, interface with the RNA recognition motif (RRM) domain of Aly/REF. Here, to determine the role the interaction of ICP27 and Aly/REF plays during infection, these residues were mutated to alanine, and a recombinant virus, WRL-A, was constructed. Virus production was reduced about 10-fold during WRL-A infection, and export of ICP27 protein and most viral mRNAs was less efficient. We conclude that interaction of ICP27 with Aly/REF contributes to efficient viral mRNA export.
Figures
References
-
- Luo MJ, Zhou Z, Magni K, Christoforides C, Rappsilber J, Mann M, Reed R. 2001. Pre-mRNA splicing and mRNA export linked by direct interactions between UAP56 and Aly. Nature 413:644–647 - PubMed
-
- Reed R. 2003. Coupling transcription, splicing and mRNA export. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 15:326–331 - PubMed
-
- Reed R, Hurt E. 2002. A conserved mRNA export machinery coupled to pre-mRNA splicing. Cell 108:523–531 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

