Mutations in FLS2 Ser-938 dissect signaling activation in FLS2-mediated Arabidopsis immunity
- PMID: 23637603
- PMCID: PMC3630090
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003313
Mutations in FLS2 Ser-938 dissect signaling activation in FLS2-mediated Arabidopsis immunity
Abstract
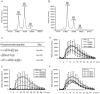
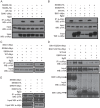
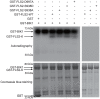
Flagellin-sensing 2 (FLS2) is a leucine-rich repeat/transmembrane domain/protein kinase (LRR-RLK) that is the plant receptor for bacterial flagellin or the flagellin-derived flg22 peptide. Previous work has shown that after flg22 binding, FLS2 releases BIK1 kinase and homologs and associates with BAK1 kinase, and that FLS2 kinase activity is critical for FLS2 function. However, the detailed mechanisms for activation of FLS2 signaling remain unclear. The present study initially identified multiple FLS2 in vitro phosphorylation sites and found that Serine-938 is important for FLS2 function in vivo. FLS2-mediated immune responses are abolished in transgenic plants expressing FLS2(S938A), while the acidic phosphomimic mutants FLS2(S938D) and FLS2(S938E) conferred responses similar to wild-type FLS2. FLS2-BAK1 association and FLS2-BIK1 disassociation after flg22 exposure still occur with FLS2(S938A), demonstrating that flg22-induced BIK1 release and BAK1 binding are not sufficient for FLS2 activity, and that Ser-938 controls other aspects of FLS2 activity. Purified BIK1 still phosphorylated purified FLS2(S938A) and FLS2(S938D) mutant kinase domains in vitro. Phosphorylation of BIK1 and homologs after flg22 exposure was disrupted in transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana plants expressing FLS2(S938A) or FLS2(D997A) (a kinase catalytic site mutant), but was normally induced in FLS2(S938D) plants. BIK1 association with FLS2 required a kinase-active FLS2, but FLS2-BAK1 association did not. Hence FLS2-BIK1 dissociation and FLS2-BAK1 association are not sufficient for FLS2-mediated defense activation, but the proposed FLS2 phosphorylation site Ser-938 and FLS2 kinase activity are needed both for overall defense activation and for appropriate flg22-stimulated phosphorylation of BIK1 and homologs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A receptor-like cytoplasmic kinase, BIK1, associates with a flagellin receptor complex to initiate plant innate immunity.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Jan 5;107(1):496-501. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0909705107. Epub 2009 Dec 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20018686 Free PMC article.
-
Inverse modulation of plant immune and brassinosteroid signaling pathways by the receptor-like cytoplasmic kinase BIK1.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Jul 16;110(29):12114-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1302154110. Epub 2013 Jul 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23818580 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid heteromerization and phosphorylation of ligand-activated plant transmembrane receptors and their associated kinase BAK1.J Biol Chem. 2010 Mar 26;285(13):9444-9451. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.096842. Epub 2010 Jan 26. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20103591 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping FLS2 function to structure: LRRs, kinase and its working bits.Protoplasma. 2013 Jun;250(3):671-81. doi: 10.1007/s00709-012-0459-6. Epub 2012 Oct 5. Protoplasma. 2013. PMID: 23053766 Review.
-
Assessing the diverse functions of BAK1 and its homologs in arabidopsis, beyond BR signaling and PTI responses.Mol Cells. 2013 Jan;35(1):7-16. doi: 10.1007/s10059-013-2255-3. Epub 2012 Dec 21. Mol Cells. 2013. PMID: 23269431 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Intracellular Ca2+ is important for flagellin-triggered defense in Arabidopsis and involves inositol polyphosphate signaling.J Exp Bot. 2017 Jun 15;68(13):3617-3628. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erx176. J Exp Bot. 2017. PMID: 28595359 Free PMC article.
-
Flagellin sensing, signaling, and immune responses in plants.Plant Commun. 2025 Jul 14;6(7):101383. doi: 10.1016/j.xplc.2025.101383. Epub 2025 May 20. Plant Commun. 2025. PMID: 40400167 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Arabidopsis CPK5 Phosphorylates the Chitin Receptor LYK5 to Regulate Plant Innate Immunity.Front Plant Sci. 2020 Jun 11;11:702. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.00702. eCollection 2020. Front Plant Sci. 2020. PMID: 32595659 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the Molecular Mechanisms of Tomatoes' Defense against Botrytis cinerea: Insights from Transcriptome Analysis of Micro-Tom and Regular Tomato Varieties.Plants (Basel). 2023 Aug 16;12(16):2965. doi: 10.3390/plants12162965. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37631176 Free PMC article.
-
The kinase LYK5 is a major chitin receptor in Arabidopsis and forms a chitin-induced complex with related kinase CERK1.Elife. 2014 Oct 23;3:e03766. doi: 10.7554/eLife.03766. Elife. 2014. PMID: 25340959 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Medzhitov R, Janeway CA Jr (1997) Innate immunity: the virtues of a nonclonal system of recognition. Cell 91: 295–298. - PubMed
-
- Boller T, Felix G (2009) A renaissance of elicitors: perception of microbe-associated molecular patterns and danger signals by pattern-recognition receptors. Annu Rev Plant Biol 60: 379–406. - PubMed
-
- Gomez-Gomez L, Boller T (2000) FLS2: an LRR receptor-like kinase involved in the perception of the bacterial elicitor flagellin in Arabidopsis . Mol Cell 5: 1003–1011. - PubMed
-
- Gomez-Gomez L, Boller T (2002) Flagellin perception: a paradigm for innate immunity. Trends Plant Sci 7: 251–256. - PubMed
-
- Chinchilla D, Zipfel C, Robatzek S, Kemmerling B, Nurnberger T, et al. (2007) A flagellin-induced complex of the receptor FLS2 and BAK1 initiates plant defence. Nature 448: 497–500. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

