Smaug/SAMD4A restores translational activity of CUGBP1 and suppresses CUG-induced myopathy
- PMID: 23637619
- PMCID: PMC3630084
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003445
Smaug/SAMD4A restores translational activity of CUGBP1 and suppresses CUG-induced myopathy
Abstract
We report the identification and characterization of a previously unknown suppressor of myopathy caused by expansion of CUG repeats, the mutation that triggers Myotonic Dystrophy Type 1 (DM1). We screened a collection of genes encoding RNA-binding proteins as candidates to modify DM1 pathogenesis using a well established Drosophila model of the disease. The screen revealed smaug as a powerful modulator of CUG-induced toxicity. Increasing smaug levels prevents muscle wasting and restores muscle function, while reducing its function exacerbates CUG-induced phenotypes. Using human myoblasts, we show physical interactions between human Smaug (SMAUG1/SMAD4A) and CUGBP1. Increased levels of SMAUG1 correct the abnormally high nuclear accumulation of CUGBP1 in myoblasts from DM1 patients. In addition, augmenting SMAUG1 levels leads to a reduction of inactive CUGBP1-eIF2α translational complexes and to a correction of translation of MRG15, a downstream target of CUGBP1. Therefore, Smaug suppresses CUG-mediated muscle wasting at least in part via restoration of translational activity of CUGBP1.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
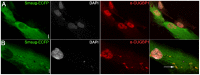

References
-
- Harper PS, Brook JD, Newman EE (2001) Myotonic dystrophy. London: W. B. Saunders. ix, 436 p. p.
-
- Osborne RJ, Thornton CA (2006) RNA-dominant diseases. Hum Mol Genet 15 Spec No 2: R162–169. - PubMed
-
- Ranum LP, Cooper TA (2006) RNA-mediated neuromuscular disorders. Annu Rev Neurosci 29: 259–277. - PubMed
-
- Sicot G, Gourdon G, Gomes-Pereira M (2011) Myotonic dystrophy, when simple repeats reveal complex pathogenic entities: new findings and future challenges. Hum Mol Genet 20: R116–123. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2R01AR052791-06/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007676/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR044387/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS078659/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 HD024064/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- T32 NS043124/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R56 NS042179/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- 2R01AR044387-12/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS042179/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- 2T32HL007676-21A1/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- IDDRC HD024064/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR052791/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- NS042179/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

