Tumor angiogenesis after heated lipiodol infusion via the hepatic artery in a rabbit model of VX2 liver cancer
- PMID: 23637861
- PMCID: PMC3634808
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061583
Tumor angiogenesis after heated lipiodol infusion via the hepatic artery in a rabbit model of VX2 liver cancer
Abstract
Objectives: This study aimed to observe the changes in tumor angiogenesis after heated lipiodol (60°C) infusion via the hepatic artery in a rabbit model of VX2 liver cancer.
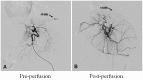
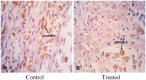
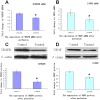
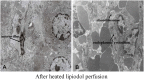
Materials and methods: Twenty rabbits with VX2 hepatic tumors were randomly divided into 2 groups (10 rabbits in each group). Under anesthesia, a trans-catheter hepatic arterial infusion was performed, and lipiodol (37°C; control group) or heated lipiodol (60°C; treated group) was injected into the hepatic arteries of the animals. Then, changes in tumor angiogenesis were assessed using the following markers and methods. 1. Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression levels in the tumor were assessed using western blotting and real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR). 2. Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) expression in the tumor was assessed through immunohistochemical staining. 3. The morphological changes in tumor vascular endothelial cells were observed using transmission electron microscopy (TEM).
Results: VEGFR and VEGF mRNA and protein expression levels were reduced in the treated group compared to the control group. PCNA protein showed reduced expression levels in the treated group compared to the control group. TEM indicated that the endothelial cell endoplasmic reticulum expanded, the chondriosome was swollen, and the endothelial cell microvilli were decreased after heated lipiodol infusion.
Conclusions: The tumor angiogenesis of rabbits with VX2 cancer was inhibited after arterial heated lipiodol infusion compared to lipiodol infusion.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Vogl TJ, Trapp M, Schroeder H, Mack M, Schuster A, et al. (2000) Transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: volumetric and morphologic CT criteria for assessment of prognosis and therapeutic success-results from a liver transplantation center. Radiology 214: 349–357. - PubMed
-
- Llovet JM, Bruix J (2003) Systematic review of randomized trials for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: Chemoembolization improves survival. Hepatology 37: 429–442. - PubMed
-
- Achenbach T, Seifert JK, Pitton MB, Schunk K, Junginger T (2002) Chemoembolization for primary liver cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol 28: 37–41. - PubMed
-
- Marelli L, Stigliano R, Triantos C, Senzolo M, Cholongitas E, et al. (2007) Transarterial therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: which technique is more effective? A systematic review of cohort and randomized studies. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 30: 6–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

