Diosmin alleviates retinal edema by protecting the blood-retinal barrier and reducing retinal vascular permeability during ischemia/reperfusion injury
- PMID: 23637907
- PMCID: PMC3634841
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061794
Diosmin alleviates retinal edema by protecting the blood-retinal barrier and reducing retinal vascular permeability during ischemia/reperfusion injury
Abstract
Background and purpose: Retinal swelling, leading to irreversible visual impairment, is an important early complication in retinal ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury. Diosmin, a naturally occurring flavonoid glycoside, has been shown to have antioxidative and anti-inflammatory effects against I/R injury. The present study was performed to evaluate the retinal microvascular protective effect of diosmin in a model of I/R injury.
Methods: Unilateral retinal I/R was induced by increasing intraocular pressure to 110 mm Hg for 60 min followed by reperfusion. Diosmin (100 mg/kg) or vehicle solution was administered intragastrically 30 min before the onset of ischemia and then daily after I/R injury until the animals were sacrificed. Rats were evaluated for retinal functional injury by electroretinogram (ERG) just before sacrifice. Retinas were harvested for HE staining, immunohistochemistry assay, ELISA, and western blotting analysis. Evans blue (EB) extravasation was determined to assess blood-retinal barrier (BRB) disruption and the structure of tight junctions (TJ) was examined by transmission electron microscopy.
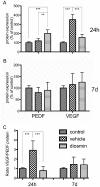
Results: Diosmin significantly ameliorated the reduction of b-wave, a-wave, and b/a ratio in ERG, alleviated retinal edema, protected the TJ structure, and reduced EB extravasation. All of these effects of diosmin were associated with increased zonular occluden-1 (ZO-1) and occludin protein expression and decreased VEGF/PEDF ratio.
Conclusions: Maintenance of TJ integrity and reduced permeability of capillaries as well as improvements in retinal edema were observed with diosmin treatment, which may contribute to preservation of retinal function. This protective effect of diosmin may be at least partly attributed to its ability to regulate the VEGF/PEDF ratio.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





Similar articles
-
Diosmin protects rat retina from ischemia/reperfusion injury.J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2012 Oct;28(5):459-66. doi: 10.1089/jop.2011.0218. Epub 2012 Apr 17. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2012. PMID: 22509733 Free PMC article.
-
Ischemia-reperfusion injury induces occludin phosphorylation/ubiquitination and retinal vascular permeability in a VEGFR-2-dependent manner.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2014 Mar;34(3):522-31. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2013.230. Epub 2014 Jan 8. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2014. PMID: 24398936 Free PMC article.
-
Α-Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormone Protects Early Diabetic Retina from Blood-Retinal Barrier Breakdown and Vascular Leakage via MC4R.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;45(2):505-522. doi: 10.1159/000487029. Epub 2018 Jan 25. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29402864
-
Postischemic leukocyte/endothelial cell interactions and microvascular barrier dysfunction in skeletal muscle: cellular mechanisms and effect of Daflon 500 mg.Int J Microcirc Clin Exp. 1997;17 Suppl 1:11-7. doi: 10.1159/000179261. Int J Microcirc Clin Exp. 1997. PMID: 9477039 Review.
-
Potential and Therapeutic Roles of Diosmin in Human Diseases.Biomedicines. 2022 May 6;10(5):1076. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10051076. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35625813 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Stasis Dermatitis: Pathophysiology, Current Treatment Paradigms, and the Use of the Flavonoid Diosmin.J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2024 Jan;17(1):15-23. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 38298753 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antioxidant Potential of Diosmin and Diosmetin against Oxidative Stress in Endothelial Cells.Molecules. 2022 Nov 25;27(23):8232. doi: 10.3390/molecules27238232. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36500323 Free PMC article.
-
Plant metabolite diosmin as the therapeutic agent in human diseases.Curr Res Pharmacol Drug Discov. 2022 Aug 13;3:100122. doi: 10.1016/j.crphar.2022.100122. eCollection 2022. Curr Res Pharmacol Drug Discov. 2022. PMID: 36568270 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Diosmin Administration in Patients with Chronic Venous Disorders on Selected Factors Affecting Angiogenesis.Molecules. 2019 Sep 12;24(18):3316. doi: 10.3390/molecules24183316. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31547271 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Characterization of mouse ocular response to a 35-day spaceflight mission: Evidence of blood-retinal barrier disruption and ocular adaptations.Sci Rep. 2019 Jun 3;9(1):8215. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-44696-0. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31160660 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Osborne NN, Casson RJ, Wood JP, Chidlow G, Graham M, et al. (2004) Retinal ischemia: mechanisms of damage and potential therapeutic strategies. Prog Retin Eye Res 23: 91–147. - PubMed
-
- Kaur C, Foulds WS, Ling EA (2008) Blood-retinal barrier in hypoxic ischaemic conditions: basic concepts, clinical features and management. Prog Retin Eye Res 27: 622–647. - PubMed
-
- Liu K, Sun T, Wang P, Liu YH, Zhang LW, et al... (2012) Effects of Erythropoietin on Blood-Brain Barrier Tight Junctions in Ischemia-Reperfusion Rats. J Mol Neurosci. - PubMed
-
- Ramelet AA (2001) Clinical benefits of Daflon 500 mg in the most severe stages of chronic venous insufficiency. Angiology 52 Suppl 1S49–56. - PubMed
-
- Smith PD (1999) Neutrophil activation and mediators of inflammation in chronic venous insufficiency. J Vasc Res 36 Suppl 124–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

