Identification and validation of novel contraction-regulated myokines released from primary human skeletal muscle cells
- PMID: 23637948
- PMCID: PMC3634789
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062008
Identification and validation of novel contraction-regulated myokines released from primary human skeletal muscle cells
Abstract
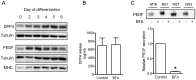
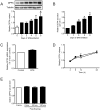
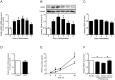
Proteins secreted by skeletal muscle, so called myokines, have been shown to affect muscle physiology and additionally exert systemic effects on other tissues and organs. Although recent profiling studies have identified numerous myokines, the amount of overlap from these studies indicates that the secretome of skeletal muscle is still incompletely characterized. One limitation of the models used is the lack of contraction, a central characteristic of muscle cells. Here we aimed to characterize the secretome of primary human myotubes by cytokine antibody arrays and to identify myokines regulated by contraction, which was induced by electrical pulse stimulation (EPS). In this study, we validated the regulation and release of two selected myokines, namely pigment epithelium derived factor (PEDF) and dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP4), which were recently described as adipokines. This study reveals that both factors, DPP4 and PEDF, are secreted by primary human myotubes. PEDF is a contraction-regulated myokine, although PEDF serum levels from healthy young men decrease after 60 min cycling at VO2max of 70%. Most interestingly, we identified 52 novel myokines which have not been described before to be secreted by skeletal muscle cells. For 48 myokines we show that their release is regulated by contractile activity. This profiling study of the human skeletal muscle secretome expands the number of myokines, identifies novel contraction-regulated myokines and underlines the overlap between proteins which are adipokines as well as myokines.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Pedersen BK (2011) Muscles and their myokines. J Exp Biol 214: 337–346. - PubMed
-
- Holloszy JO, Coyle EF (1984) Adaptations of skeletal muscle to endurance exercise and their metabolic consequences. J Appl Physiol 56: 831–838. - PubMed
-
- Ross A, Leveritt M (2001) Long-term metabolic and skeletal muscle adaptations to short-sprint training: implications for sprint training and tapering. Sports Med 31: 1063–1082. - PubMed
-
- Petersen AM, Pedersen BK (2005) The anti-inflammatory effect of exercise. J Appl Physiol 98: 1154–1162. - PubMed
-
- Kersten S, Lichtenstein L, Steenbergen E, Mudde K, Hendriks HF, et al. (2009) Caloric restriction and exercise increase plasma ANGPTL4 levels in humans via elevated free fatty acids. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 29: 969–974. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

