miR-221 promotes tumorigenesis in human triple negative breast cancer cells
- PMID: 23637992
- PMCID: PMC3634767
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062170
miR-221 promotes tumorigenesis in human triple negative breast cancer cells
Retraction in
-
Retraction: miR-221 Promotes Tumorigenesis in Human Triple Negative Breast Cancer Cells.PLoS One. 2017 Apr 10;12(4):e0175869. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0175869. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28394920 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
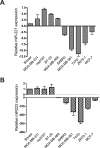
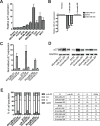
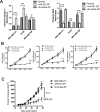
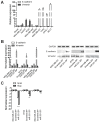
Patients with triple-negative breast cancers (TNBCs) typically have a poor prognosis. TNBCs are characterized by their resistance to apoptosis, aggressive cellular proliferation, migration and invasion, and currently lack molecular markers and effective targeted therapy. Recently, miR-221/miR-222 have been shown to regulate ERα expression and ERα-mediated signaling in luminal breast cancer cells, and also to promote EMT in TNBCs. In this study, we characterized the role of miR-221 in a panel of TNBCs as compared to other breast cancer types. miR-221 knockdown not only blocked cell cycle progression, induced cell apoptosis, and inhibited cell proliferation in-vitro but it also inhibited in-vivo tumor growth by targeting p27(kip1). Furthermore, miR-221 knockdown inhibited cell migration and invasion by altering E-cadherin expression, and its regulatory transcription factors Snail and Slug in human TNBC cell lines. Therefore, miR-221 functions as an oncogene and is essential in regulating tumorigenesis in TNBCs both in vitro as well as in vivo.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116: 281–297. - PubMed
-
- Lim LP, Lau NC, Garrett-Engele P, Grimson A, Schelter JM, et al. (2005) Microarray analysis shows that some microRNAs downregulate large numbers of target mRNAs. Nature 433: 769–773. - PubMed
-
- Lewis BP, Shih IH, Jones-Rhoades MW, Bartel DP, Burge CB (2003) Prediction of mammalian microRNA targets. Cell 115: 787–798. - PubMed
-
- Esquela-Kerscher A, Slack FJ (2006) Oncomirs - microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 6: 259–269. - PubMed
-
- Ambros V (2004) The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 431: 350–355. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

