Small GTPase Rab40c associates with lipid droplets and modulates the biogenesis of lipid droplets
- PMID: 23638186
- PMCID: PMC3640056
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0063213
Small GTPase Rab40c associates with lipid droplets and modulates the biogenesis of lipid droplets
Abstract
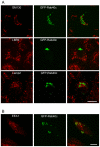
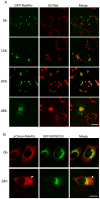
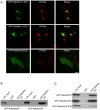
The subcellular location and cell biological function of small GTPase Rab40c in mammalian cells have not been investigated in detail. In this study, we demonstrated that the exogenously expressed GFP-Rab40c associates with lipid droplets marked by neutral lipid specific dye Oil red or Nile red, but not with the Golgi or endosomal markers. Further examination demonstrated that Rab40c is also associated with ERGIC-53 containing structures, especially under the serum starvation condition. Rab40c is increasingly recruited to the surface of lipid droplets during lipid droplets formation and maturation in HepG2 cells. Rab40c knockdown moderately decreases the size of lipid droplets, suggesting that Rab40c is involved in the biogenesis of lipid droplets. Stimulation for adipocyte differentiation increases the expression of Rab40c in 3T3-L1 cells. Rab40c interacts with TIP47, and is appositionally associated with TIP47-labeled lipid droplets. In addition, over-expression of Rab40c causes the clustering of lipid droplets independent of its GTPase activity, but completely dependent of the intact SOCS box domain of Rab40c. In addition, Rab40c displayed self-interaction as well as interaction with TIP47 and the SOCS box is essential for its ability to induce clustering of lipid droplets. Our results suggest that Rab40c is a novel Rab protein associated with lipid droplets, and is likely involved in modulating the biogenesis of lipid droplets.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





Similar articles
-
Analysis of biogenesis of lipid droplets by examining Rab40c associating with lipid droplets.Methods Mol Biol. 2015;1270:125-35. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-2309-0_10. Methods Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25702114
-
S3-12, Adipophilin, and TIP47 package lipid in adipocytes.J Biol Chem. 2005 May 13;280(19):19146-55. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M500978200. Epub 2005 Feb 24. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15731108
-
Characterization of Rab18, a lipid droplet-associated small GTPase.Methods Enzymol. 2008;438:109-29. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(07)38008-7. Methods Enzymol. 2008. PMID: 18413244
-
[Function of PAT family proteins in the lipid metabolism].Sheng Li Ke Xue Jin Zhan. 2006 Apr;37(2):103-7. Sheng Li Ke Xue Jin Zhan. 2006. PMID: 16850611 Review. Chinese.
-
Thematic review series: adipocyte biology. The perilipin family of structural lipid droplet proteins: stabilization of lipid droplets and control of lipolysis.J Lipid Res. 2007 Dec;48(12):2547-59. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R700014-JLR200. Epub 2007 Sep 18. J Lipid Res. 2007. PMID: 17878492 Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of the proteome of cytoplasmic lipid droplets in mouse enterocytes after a dietary fat challenge.PLoS One. 2015 May 18;10(5):e0126823. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0126823. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25992653 Free PMC article.
-
The evolutionary landscape of the Rab family in chordates.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019 Oct;76(20):4117-4130. doi: 10.1007/s00018-019-03103-7. Epub 2019 Apr 26. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 31028425 Free PMC article.
-
Peripheral Neuropathy and Decreased Locomotion of a RAB40B Mutation in Human and Model Animals.Exp Neurobiol. 2023 Dec 31;32(6):410-422. doi: 10.5607/en23027. Exp Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 38196136 Free PMC article.
-
Consequences of Rab GTPase dysfunction in genetic or acquired human diseases.Small GTPases. 2018 Mar 4;9(1-2):158-181. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2017.1397833. Epub 2017 Dec 28. Small GTPases. 2018. PMID: 29239692 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-Wide siRNA Screen Identifies Complementary Signaling Pathways Involved in Listeria Infection and Reveals Different Actin Nucleation Mechanisms during Listeria Cell Invasion and Actin Comet Tail Formation.mBio. 2015 May 19;6(3):e00598-15. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00598-15. mBio. 2015. PMID: 25991686 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

