Effects of glycyl-glutamine dipeptide supplementation on myocardial damage and cardiac function in rats after severe burn injury
- PMID: 23638213
- PMCID: PMC3638092
Effects of glycyl-glutamine dipeptide supplementation on myocardial damage and cardiac function in rats after severe burn injury
Abstract
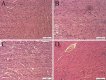
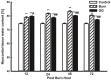
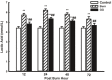
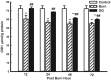
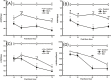
Glutamine decreases myocardial damage in ischemia/reperfusion injury. However, the cardioprotective effect of glutamine after burn injury remains unclear. Present study was to explore the protective effect of glycyl-glutamine dipeptide on myocardial damage in severe burn rats. Seventy-two Wistar rats were randomly divided into three groups: normal control (C), burned control (B) and glycyl-glutamine dipeptide-treated (GG) groups. B and GG groups were inflicted with 30% total body surface area of full thickness burn. The GG group was given 1.5 g/kg glycyl-glutamine dipeptide per day and the B group was given the same dose of alanine via intraperitoneal injection for 3 days. The serum CK, LDH, AST, and, blood lactic acid levels, as well as the myocardium ATP and GSH contents, were measured. The indices of cardiac contractile function and histopathological change were analyzed at 12, 24, 48, and 72 post-burn hours (PBH). The serum CK, LDH, AST and blood lactic acid levels increased, and the myocardium ATP and GSH content decreased in both burned groups. Compared with B group, the CK, LDH, AST and blood lactic acid levels reduced, myocardium ATP and GSH content increased in GG group. Moreover, the inhibition of cardiac contractile function and myocardial histopathological damage were reduced significantly in GG group. We conclude that myocardial histological structure and function were damaged significantly after burn injury, glycyl-glutamine dipeptide supplementation is beneficial to myocardial preservation by improving cardiocyte energy metabolism, increasing ATP and glutathione synthesis.
Keywords: GSH; Glycyl-glutamine dipeptide; burns; energy metabolism; myocardial damage; rat.
Figures
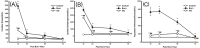

Similar articles
-
Effects of glutamine treatment on myocardial damage and cardiac function in rats after severe burn injury.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2012;5(7):651-9. Epub 2012 Sep 5. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2012. PMID: 22977661 Free PMC article.
-
[Protective effects of glycyl-glutamine dipeptide supplement on the heart function in burn rats].Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2007 Aug;23(4):244-8. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2007. PMID: 18095544 Chinese.
-
Effects of glycine supplementation on myocardial damage and cardiac function after severe burn.Burns. 2013 Jun;39(4):729-35. doi: 10.1016/j.burns.2012.09.006. Epub 2012 Oct 1. Burns. 2013. PMID: 23036846
-
Single dose of glutamine enhances myocardial tissue metabolism, glutathione content, and improves myocardial function after ischemia-reperfusion injury.JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2003 Nov-Dec;27(6):396-403. doi: 10.1177/0148607103027006396. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2003. PMID: 14621120
-
Puerarin attenuates severe burn-induced acute myocardial injury in rats.Burns. 2015 Dec;41(8):1748-1757. doi: 10.1016/j.burns.2015.06.001. Epub 2015 Oct 26. Burns. 2015. PMID: 26514700
Cited by
-
Glutamine provides effective protection against deltamethrin-induced acute hepatotoxicity in rats but not against nephrotoxicity.Med Sci Monit. 2015 Apr 19;21:1107-14. doi: 10.12659/MSM.893180. Med Sci Monit. 2015. PMID: 25890620 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects of l-glutamine against toxicity of deltamethrin in the cerebral tissue.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2016 Apr 21;12:1005-11. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S104011. eCollection 2016. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2016. PMID: 27143900 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of ageing and hypertension on the expression and activity of PEPT2 in normal and hypertrophic hearts.Amino Acids. 2021 Feb;53(2):183-193. doi: 10.1007/s00726-020-02936-y. Epub 2021 Jan 6. Amino Acids. 2021. PMID: 33404911
-
Rosuvastatin Attenuates Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury via Upregulating miR-17-3p-Mediated Autophagy.Cell Reprogram. 2019 Dec;21(6):323-330. doi: 10.1089/cell.2018.0053. Epub 2019 Nov 15. Cell Reprogram. 2019. PMID: 31730378 Free PMC article.
-
[A prospectively randomized controlled study of the effects of intensive insulin therapy combined with glutamine on nutritional metabolism, inflammatory response, and hemodynamics in severe burn patients].Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2021 Sep 20;37(9):821-830. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501120-20210428-00159. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34645147 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. Chinese.
References
-
- Latenser BA. Critical care of the burn patient: the first 48 hours. Crit Care Med. 2009;37:2819–2826. - PubMed
-
- Huang Y, Li Z, Yang Z. Roles of ischemia and hypoxia and the molecular pathogenesis of post-burn cardiac shock. Burns. 2003;29:828–833. - PubMed
-
- Huang YS, Yang ZC, Yan BG, Yang JM, Chen FM, Crowther RS, Li A. Pathogenesis of early cardiac myocyte damage after severe burns. J Trauma. 1999;46:428–432. - PubMed
-
- Jiang L, Qin X, Zhong X, Liu L, Lu Y, Fan L, He Z, Chen Q. Glycine-induced cytoprotection is mediated by ERK1/2 and AKT in renal cells with ATP depletion. Eur J Cell Biol. 2011;90:333–341. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
