Galectin-3: a novel protein in cerebellar hemangioblastoma
- PMID: 23638216
- PMCID: PMC3638095
Galectin-3: a novel protein in cerebellar hemangioblastoma
Abstract
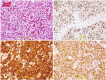
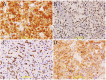
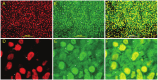
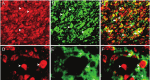
Hemangioblastoma (HB), a rare neoplasm of uncertain histogenesis, is characterized histologically by the presence of vacuolated; lipid-containing cells 'stromal cells' and a well developed, fine capillary network. Stromal cells are the neoplastic component of this tumor. Five-um sections were stained using streptavidin- biotin immunoperoxidase and immunofluorescent techniques. The stromal cells were uniformly "HIF-1α, Galectin-3, VEGF, VEGFR, WT-1, and bcl2," positive. Endothelial cells but not stromal cells were uniformly immunoreactive to CD31. Co-localization of HIF-1α with galectin-3 and VEGF as well as galectin-3 with VEGF in stromal cells is confirmed by immunofluorescent technique. In conclusion, the development of HB is multi-factorial and the expression of galectin-3 correlates with the expression of HIF-1α and VEGF. Galectin-3 can be used as a marker for the diagnosis of HB as well as it can be a valuable candidate for future targeting immunotherapy.
Keywords: CNS neoplasms; HIF; galectin-3; hemangioblastoma.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Stromal cell-derived factor-1alpha and CXCR4 expression in hemangioblastoma and clear cell-renal cell carcinoma: von Hippel-Lindau loss-of-function induces expression of a ligand and its receptor.Cancer Res. 2005 Jul 15;65(14):6178-88. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-4406. Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 16024619
-
Up-regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor in stromal cells of hemangioblastomas is correlated with up-regulation of the transcription factor HRF/HIF-2alpha.Am J Pathol. 1998 Jul;153(1):25-9. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9440(10)65541-1. Am J Pathol. 1998. PMID: 9665461 Free PMC article.
-
Stromal cells in hemangioblastoma: neuroectodermal differentiation and morphological similarities to ependymoma.Pathol Int. 2005 Jul;55(7):377-85. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.2005.01841.x. Pathol Int. 2005. PMID: 15982211
-
Cerebellar ependymoma with overlapping features of clear-cell and tanycytic variants mimicking hemangioblastoma: a case report and literature review.Diagn Pathol. 2017 Mar 20;12(1):28. doi: 10.1186/s13000-017-0619-2. Diagn Pathol. 2017. PMID: 28320419 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Accelerated growth of hemangioblastoma in pregnancy: the role of proangiogenic factors and upregulation of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) in a non-oxygen-dependent pathway.Neurosurg Rev. 2019 Jun;42(2):209-226. doi: 10.1007/s10143-017-0910-4. Epub 2017 Oct 13. Neurosurg Rev. 2019. PMID: 29027018 Review.
Cited by
-
Hypoxia Up-Regulates Galectin-3 in Mammary Tumor Progression and Metastasis.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 29;10(7):e0134458. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0134458. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26222311 Free PMC article.
-
Combined transcriptomic and lipidomic analysis reveals aberrant lipid metabolism in central nervous system hemangioblastomas.Sci Rep. 2021 Jan 14;11(1):1314. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-80263-8. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33446752 Free PMC article.
-
Sporadic Hemangioblastoma Arising from the Infundibulum.J Radiol Case Rep. 2017 May 31;11(5):1-6. doi: 10.3941/jrcr.v11i5.2981. eCollection 2017 May. J Radiol Case Rep. 2017. PMID: 29299088 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a panel of complex autoantigens (LGALS3, PHB2, MUC1, and GK2) in combination with CA15-3 for the diagnosis of early-stage breast cancer.Tumour Biol. 2016 Jan;37(1):1309-17. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-3932-y. Epub 2015 Aug 21. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26289852
-
A Challenge in Diagnosis of Cerebellar Hemangioblastoma.Cureus. 2022 Jan 29;14(1):e21713. doi: 10.7759/cureus.21713. eCollection 2022 Jan. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 35242478 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ishizawa K, Komori T, Hirose T. Stromal cells in hemangioblastoma: neuroectodermal differentiation and morphological similarities to ependymoma. Pathol Int. 2005;55:377–385. - PubMed
-
- Lantos PL, Louis DN, Rosenblum MK, Kleihues P. Tumours of the nervous system. In: Graham DI, Lantos PL, editors. Greenfield’s Neuropathology. 7th edition. London: Arnold; 2002. pp. 767–1052.
-
- Barondes SH, Cooper DN, Gitt MA, Leffler H. Galectins: structure and function of a large family of animal lectins. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:20807–20810. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
