SUSTAINED TL1A (TNFSF15) EXPRESSION ON BOTH LYMPHOID AND MYELOID CELLS LEADS TO MILD SPONTANEOUS INTESTINAL INFLAMMATION AND FIBROSIS
- PMID: 23638306
- PMCID: PMC3638202
- DOI: 10.1556/EuJMI.3.2013.1.2
SUSTAINED TL1A (TNFSF15) EXPRESSION ON BOTH LYMPHOID AND MYELOID CELLS LEADS TO MILD SPONTANEOUS INTESTINAL INFLAMMATION AND FIBROSIS
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Sustained TL1A (TNFSF15) expression on both lymphoid and myeloid cells leads to mild spontaneous intestinal inflammation and fibrosis (DOI: 10.1556/EuJMI.3.2013.1.2).Eur J Microbiol Immunol (Bp). 2013 Jun;3(2):141. doi: 10.1556/EuJMI.3.2013.2.8. Epub 2013 Jun 5. Eur J Microbiol Immunol (Bp). 2013. PMID: 24265931 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
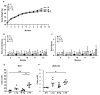
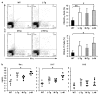
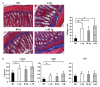
TL1A is a member of the TNF superfamily, and its expression is increased in the mucosa of inflammatory bowel disease patients. Moreover, patients with certain TNFSF15 variants over-express TL1A and have a higher risk of developing strictures in the small intestine. Consistently, mice with sustained Tl1a expression in either lymphoid or myeloid cells develop spontaneous ileitis and increased intestinal collagen deposition. Transgenic (Tg) mice with constitutive Tl1a expression in both lymphoid and myeloid cells were generated to assess their in vivo consequence. Constitutive expression of Tl1a in both lymphoid and myeloid cells showed increased spontaneous ileitis and collagen deposition than WT mice. T cells with constitutive expression of Tl1a in both lymphoid and myeloid cells were found to have a more activated phenotype, increased gut homing marker CCR9 expression, and enhanced Th1 and Th17 cytokine activity than WT mice. Although no differences in T cell activation marker, Th1 or Th17 cytokine activity, ileitis, or collagen deposition were found between constitutive Tl1a expression in lymphoid only, myeloid only, or combined lymphoid and myeloid cells. Double hemizygous Tl1a-Tg mice appeared to have worsened ileitis and intestinal fibrosis. Our findings confirm that TL1A-DR3 interaction is involved in T cell-dependent ileitis and fibrosis.
Keywords: fibrosis; ileitis; mucosal inflammation; transgenic.
Figures


References
-
- Barrett R, Zhang X, Koon HW, Vu M, Chang JY, Yeager N, Nguyen MA, Michelsen KS, Berel D, Pothoulakis C, Targan SR, Shih DQ. Constitutive TL1A expression under colitogenic conditions modulates the severity and location of gut mucosal inflammation and induces fibrostenosis. The American journal of pathology. 2012 Feb 1;180(2) doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.10.026. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
