Relationship between the proteasomal system and autophagy
- PMID: 23638318
- PMCID: PMC3627065
Relationship between the proteasomal system and autophagy
Abstract
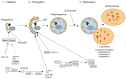
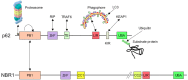
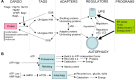
TWO MAJOR PATHWAYS DEGRADE MOST CELLULAR PROTEINS IN EUKARYOTIC CELLS: the ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS), which usually degrades the majority of proteins, and autophagy, primarily responsible for the degradation of most long-lived or aggregated proteins and cellular organelles. Disruption of these processes can contribute to pathology of a variety of diseases. Further, both pathways are critical for the maintenance of several aspects of cellular homeostasis, but, until recently, were thought to be largely distinct. Recent advances in this field, however, now strongly suggest that their activities are carefully orchestrated through several interfacing elements that are presented and discussed in this review.
Keywords: Proteasome; autophagy; homeostasis; ubiquitin.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Impaired proteasomal degradation enhances autophagy via hypoxia signaling in Drosophila.BMC Cell Biol. 2013 Jun 25;14:29. doi: 10.1186/1471-2121-14-29. BMC Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23800266 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk Between Mammalian Autophagy and the Ubiquitin-Proteasome System.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2018 Oct 2;6:128. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2018.00128. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2018. PMID: 30333975 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The ubiquitin-proteasome system and autophagy: Coordinated and independent activities.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2016 Oct;79:403-418. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2016.07.019. Epub 2016 Jul 20. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27448843 Review.
-
The Intertwining of Autophagy and the Ubiquitin Proteasome System in Podocyte (Patho)Physiology.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2021 Sep 15;55(S4):68-95. doi: 10.33594/000000432. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2021. PMID: 34523304 Review.
-
The ubiquitin-proteasome system in cardiac dysfunction.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008 Dec;1782(12):749-63. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2008.06.009. Epub 2008 Jun 25. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008. PMID: 18634872 Review.
Cited by
-
Functional characterization of EI24-induced autophagy in the degradation of RING-domain E3 ligases.Autophagy. 2016 Nov;12(11):2038-2053. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2016.1217371. Epub 2016 Aug 19. Autophagy. 2016. PMID: 27541728 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Autophagy and lncRNAs in the Maintenance of Cancer Stem Cells.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Mar 11;13(6):1239. doi: 10.3390/cancers13061239. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33799834 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The ubiquitin ligase tripartite-motif-protein 32 is induced in Duchenne muscular dystrophy.Lab Invest. 2016 Aug;96(8):862-71. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2016.63. Epub 2016 Jun 13. Lab Invest. 2016. PMID: 27295345
-
Apoptosis and Autophagy in Picornavirus Infection.Front Microbiol. 2019 Sep 3;10:2032. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02032. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31551969 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identifying Potential Mitochondrial Proteome Signatures Associated with the Pathogenesis of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension in the Rat Model.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Feb 21;2022:8401924. doi: 10.1155/2022/8401924. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 35237384 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schoenheimer R, Ratner S, Rittenberg D. Studies in protein metabolism: VII. The metabolism of tyrosines. J Biol Chem. 1939;127:333–344.
-
- Rock KL, Gramm C, Rothstein L, Clarck K, Stein R, Dick L, Hwang D, Goldberg AL. Inhibitors of the proteasome block the degradation of most cell proteins and the generation of peptides presented on MHC class I molecules. Cell. 1994;78:761–771. - PubMed
-
- Hershko A, Ciechanover A. The ubiquitin system. Annu Rev Biochem. 1998;67:425–479. - PubMed
-
- Ciechanover A. Intracellular protein degradation: From a vague idea thru the lysosome and the ubiquitin-proteasome system and onto human diseases and drug targeting. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012;1824:3–13. - PubMed
-
- Pickart CM, Eddins MJ. Ubiquitin: structures, functions, mechanisms. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004;1695:55–72. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
