Treatment of intractable orbital implant exposure with a large conjunctival defect by secondary insertion of the implant after preceding dermis fat graft
- PMID: 23638423
- PMCID: PMC3633760
- DOI: 10.3980/j.issn.2222-3959.2013.02.17
Treatment of intractable orbital implant exposure with a large conjunctival defect by secondary insertion of the implant after preceding dermis fat graft
Abstract
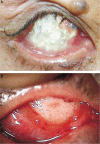
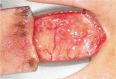
Aim: To report a procedure and results of a two-stage operation to manage intractable extensive orbital implant exposure with a large conjunctival defect which was difficult to treat with dermis fat grafts due to repeated graft necrosis.
Methods: A retrospective chart review of four patients who had extensive orbital implant exposures with large conjunctival defects and had past histories of repeated autologous or preserved dermis graft failures was done. As a first-stage operation, the problematic pre-existing orbital implants were removed and autologous dermis fat grafts alone were performed on the defect area. Four months later, new orbital implants were secondarily inserted after confirmation of graft survival. The size of the conjunctival defects and state of the extraocular muscles were checked preoperatively. Success of the operations and complications were investigated.
Results: The mean size of the conjuctival defects was 17.3mm×16.0mm, and the mean time from the initial diagnosis of orbital implant exposure to implant removal and autologous dermis fat graft was 20.8 months. After implant removal and autologous dermis fat graft, no graft necrosis was observed in any patients. Also, implant exposure or fornix shortening was not observed in any patients after new orbital implant insertion.
Conclusion: The secondary insertion of a new orbital implant after pre-existing implant removal and preceding dermis fat graft is thought to be an another selective management of intractable orbital implant exposure in which dermis fat grafts persistently fail.
Keywords: conjunctival defect; dermis fat graft; orbital implant exposure.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Surgical outcomes of acellular human dermal grafts for large conjunctiva defects in orbital implant insertion.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2013 Jul;251(7):1849-54. doi: 10.1007/s00417-013-2365-9. Epub 2013 May 19. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2013. PMID: 23686224
-
Exposed porous orbital implants treated with simultaneous secondary implant and dermis fat graft.Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. 2010 Jul-Aug;26(4):273-6. doi: 10.1097/IOP.0b013e3181bf24db. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. 2010. PMID: 20523255
-
Long-term complications of different porous orbital implants: a 21-year review.Br J Ophthalmol. 2017 May;101(5):681-685. doi: 10.1136/bjophthalmol-2016-308932. Epub 2016 Jul 29. Br J Ophthalmol. 2017. PMID: 27474155 Review.
-
Amniotic membrane transplantation for conjunctival epithelization of exposed dermis-fat [corrected] graft.Orbit. 2007 Jun;26(2):133-5. doi: 10.1080/01676830600977400. Orbit. 2007. PMID: 17613863
-
Complications of dermis-fat orbital implantation.Adv Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. 1990;8:170-81. Adv Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. 1990. PMID: 2248708 Review.
Cited by
-
In vitro adherence of conjunctival bacteria to different oculoplastic materials.Int J Ophthalmol. 2018 Dec 18;11(12):1895-1901. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2018.12.03. eCollection 2018. Int J Ophthalmol. 2018. PMID: 30588419 Free PMC article.
-
Single-Stage Orbital Socket Reconstruction Using the Oversized Dermis Fat Graft and the 22 mm Silicone Orbital Implant after an Extended Enucleation.Case Rep Ophthalmol Med. 2018 Dec 4;2018:8954193. doi: 10.1155/2018/8954193. eCollection 2018. Case Rep Ophthalmol Med. 2018. PMID: 30627470 Free PMC article.
-
Helium-neon laser therapy in the treatment of hydroxyapatite orbital implant exposure: A superior option.Exp Ther Med. 2015 Sep;10(3):1074-1078. doi: 10.3892/etm.2015.2589. Epub 2015 Jun 23. Exp Ther Med. 2015. PMID: 26622442 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kim YD, Goldberg RA, Shorr N, Steinsapir KD. Management of exposed hydroxyapatite orbital implants. Ophthalmology. 1994;101(10):1709–1715. - PubMed
-
- Oestreicher JH. Treatment of exposed coral implant after failed scleral patch graft. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 1994;10(2):110–113. - PubMed
-
- Guberina C, Hornblass A, Smith B. Pitfalls of autogenous lipodermal implantation to the orbit. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 1987;3(2):65–70. - PubMed
-
- Custer PL, Trinkaus KM. Porous implant exposure: incidence, management, and morbidity. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 2007;23(1):1–7. - PubMed
-
- Yoon JS, Lew H, Kim SJ, Lee SY. Exposure rate of hydroxyapatite orbital implants a 15-year experience of 802 cases. Ophthalmology. 2008;115(3):566–572. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
