Potential therapeutic effects of pigment epithelium-derived factor for treatment of diabetic retinopathy
- PMID: 23638428
- PMCID: PMC3633765
- DOI: 10.3980/J.ISSN.2222-3959.2013.02.22
Potential therapeutic effects of pigment epithelium-derived factor for treatment of diabetic retinopathy
Abstract
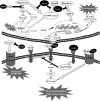
Diabetic retinopathy (DR), a major micro-vascular complication of diabetes, has emerged as a leading cause of visual impairment and blindness among working adults in the worldwide. The pathobiology of DR involves multiple molecular pathways and is characterized chronic neurovascular degeneration. Current approaches to prevent or to treat DR are still far from satisfactory. Therefore, it is important to develop new therapeutic strategies for the prevention and treatment to DR. Pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF), a 50-kDa secreted glycoprotein, has been described as a multi-functional protein. Some emerging evidences indicate that PEDF are able to target multiple pathways exerting neurotropic, neuroprotective, anti-angiogenic, antivasopermeability, anti-inflammation, anti-thrombogenic and anti-oxidative effects in DR. In this review, we addressed the functions of PEDF in different pathways, which could lead to potential therapeutics on the treatment to DR.
Keywords: diabetic retinopathy; molecular therapeutics; pigment epithelium derived factor; pleiotropic functions.
Figures
References
-
- Fong DS, Aiello L, Gardner TW, King GL, Blankenship G, Cavallerano JD, Ferris III FL, Klein R. Retinopathy in diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2004;27(1):84–87. - PubMed
-
- Yang SH, Dou KF, Song WJ. Prevalence of diabetes among men and women in China. N Engl J Med. 2010;362(25):2425–2426. - PubMed
-
- Mohamed Q, Gillies MC, Wong TY. Management of diabetic retinopathy: a systematic review. JAMA. 2007;298(8):902–916. - PubMed
-
- Becerra SP. Focus on molecules: pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) Exp Eye Res. 2006;82(5):739–740. - PubMed
-
- Filleur S, Nelius T, de Riese W, Kennedy RC. Characterization of PEDF: a multi-functional serpin family protein. J Cell Biochem. 2009;106(5):769–775. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
