Death receptors as targets in cancer
- PMID: 23638798
- PMCID: PMC3753832
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.12238
Death receptors as targets in cancer
Abstract
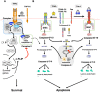
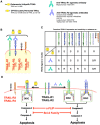
Anti-tumour therapies based on the use pro-apoptotic receptor agonists, including TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) or monoclonal antibodies targeting TRAIL-R1 or TRAIL-R2, have been disappointing so far, despite clear evidence of clinical activity and lack of adverse events for the vast majority of these compounds, whether combined or not with conventional or targeted anti-cancer therapies. This brief review aims at discussing the possible reasons for the lack of apparent success of these therapeutic approaches and at providing hints in order to rationally design optimal protocols based on our current understanding of TRAIL signalling regulation or resistance for future clinical trials.
Linked articles: This article is part of a themed section on Emerging Therapeutic Aspects in Oncology. To view the other articles in this section visit http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/bph.2013.169.issue-8.
Keywords: Fas; TNF-receptor superfamily; TRAIL; apoptosis; resistance; therapy; tumour targeting.
© 2013 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures

References
-
- Ashkenazi A, Dixit VM. Death receptors: signaling and modulation. Science. 1998;281:1305–1308. - PubMed
-
- Ashkenazi A, Holland P, Eckhardt SG. Ligand-based targeting of apoptosis in cancer: the potential of recombinant human apoptosis ligand 2/tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (rhApo2L/TRAIL) J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:3621–3630. - PubMed
-
- Bagnoli M, Ambrogi F, Pilotti S, Alberti P, Ditto A, Barbareschi M, et al. c-FLIPL expression defines two ovarian cancer patient subsets and is a prognostic factor of adverse outcome. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2009;16:443–453. - PubMed
-
- Baritaki S, Huerta-Yepez S, Sakai T, Spandidos DA, Bonavida B. Chemotherapeutic drugs sensitize cancer cells to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis: up-regulation of DR5 and inhibition of Yin Yang 1. Mol Cancer Ther. 2007;6:1387–1399. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

