Protein phosphatase 2A: a target for anticancer therapy
- PMID: 23639323
- PMCID: PMC3913484
- DOI: 10.1016/S1470-2045(12)70558-2
Protein phosphatase 2A: a target for anticancer therapy
Abstract
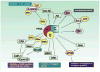
Protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A), one of the main serine-threonine phosphatases in mammalian cells, maintains cell homoeostasis by counteracting most of the kinase-driven intracellular signalling pathways. Unrestrained activation of oncogenic kinases together with inhibition of tumour suppressors is often required for development of cancer. PP2A has been shown to be genetically altered or functionally inactivated in many solid cancers and leukaemias, and is therefore a tumour suppressor. For example, the phosphatase activity of PP2A is suppressed in chronic myeloid leukaemia and other malignancies characterised by aberrant activity of oncogenic kinases. Preclinical studies show that pharmacological restoration of PP2A tumour-suppressor activity by PP2A-activating drugs (eg, FTY720) effectively antagonises cancer development and progression. Here, we discuss PP2A as a druggable tumour suppressor in view of the possible introduction of PP2A-activating drugs into anticancer therapeutic protocols.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Tsatsanis C, Spandidos DA. The role of oncogenic kinases in human cancer (Review) Int J Mol Med. 2000;5(6):583–90. Epub 2000/05/17. - PubMed
-
- Look AT. Oncogenic transcription factors in the human acute leukemias. Science. 1997;278(5340):1059–64. Epub 1997/11/14. - PubMed
-
- Yip KW, Reed JC. Bcl-2 family proteins and cancer. Oncogene. 2008;27(50):6398–406. Epub 2008/10/29. - PubMed
-
- Sherr CJ. Principles of tumor suppression. Cell. 2004;116(2):235–46. Epub 2004/01/28. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

