Multi-omic data integration links deleted in breast cancer 1 (DBC1) degradation to chromatin remodeling in inflammatory response
- PMID: 23639857
- PMCID: PMC3734575
- DOI: 10.1074/mcp.M112.026138
Multi-omic data integration links deleted in breast cancer 1 (DBC1) degradation to chromatin remodeling in inflammatory response
Abstract
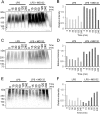
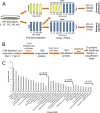
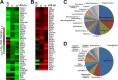
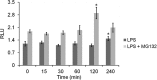
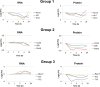
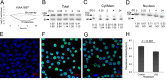
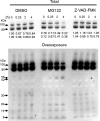
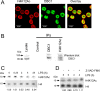
This study investigated the dynamics of ubiquitinated proteins after the inflammatory stimulation of RAW 264.7 macrophage-like cells with bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Ubiquitination is a common protein post-translational modification that regulates many key cellular functions. We demonstrated that levels of global ubiquitination and K48 and K63 polyubiquitin chains change after lipopolysaccharide stimulation. Quantitative proteomic analysis identified 1199 ubiquitinated proteins, 78 of which exhibited significant changes in ubiquitination levels following stimulation. Integrating the ubiquitinome data with global proteomic and transcriptomic results allowed us to identify a subset of 88 proteins that were targeted for degradation after lipopolysaccharide stimulation. Using cellular assays and Western blot analyses, we biochemically validated DBC1 (a histone deacetylase inhibitor) as a degradation substrate that is targeted via an orchestrated mechanism utilizing caspases and the proteasome. The degradation of DBC1 releases histone deacetylase activity, linking lipopolysaccharide activation to chromatin remodeling in caspase- and proteasome-mediated signaling.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Proteomic Profile of Deleted in Breast Cancer 1 (DBC1) Interactions Points to a Multifaceted Regulation of Gene Expression.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2016 Mar;15(3):791-809. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M115.054619. Epub 2015 Dec 9. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2016. PMID: 26657080 Free PMC article.
-
Cereblon suppresses the lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response by promoting the ubiquitination and degradation of c-Jun.J Biol Chem. 2018 Jun 29;293(26):10141-10157. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.002246. Epub 2018 May 10. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29748389 Free PMC article.
-
Deleted in breast cancer 1 (DBC1) deficiency results in apoptosis of breast cancer cells through impaired responses to UV-induced DNA damage.Cancer Lett. 2013 Jun 10;333(2):180-6. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2013.01.026. Epub 2013 Jan 22. Cancer Lett. 2013. PMID: 23352644
-
Role of ubiquitination in the DNA damage response: proteomic analysis to identify new DNA-damage-induced ubiquitinated proteins.Biochem Soc Trans. 2010 Feb;38(Pt 1):87-91. doi: 10.1042/BST0380087. Biochem Soc Trans. 2010. PMID: 20074041 Review.
-
The complexity of recognition of ubiquitinated substrates by the 26S proteasome.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Jan;1843(1):86-96. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2013.07.007. Epub 2013 Jul 18. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 23872423 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of Salmonella Typhimurium Deubiquitinase SseL Substrates by Immunoaffinity Enrichment and Quantitative Proteomic Analysis.J Proteome Res. 2015 Sep 4;14(9):4029-38. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.5b00574. Epub 2015 Aug 6. J Proteome Res. 2015. PMID: 26147956 Free PMC article.
-
Alterations of host cell ubiquitination machinery by pathogenic bacteria.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2015 Feb 27;5:17. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2015.00017. eCollection 2015. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25774357 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

