4-Hydroxy-2-nonenal enhances tissue factor activity in human monocytic cells via p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activation-dependent phosphatidylserine exposure
- PMID: 23640483
- PMCID: PMC3883589
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.113.300972
4-Hydroxy-2-nonenal enhances tissue factor activity in human monocytic cells via p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activation-dependent phosphatidylserine exposure
Abstract
Objective: 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal (HNE) is one of the major aldehydes formed during lipid peroxidation and is believed to play a role in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. The objective of the present study is to investigate the effect of HNE on tissue factor (TF) procoagulant activity expressed on cell surfaces.
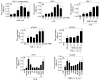
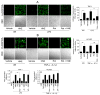
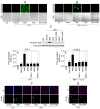
Approach and results: TF activity and antigen levels on intact cells were measured using factor Xa generation and TF monoclonal antibody binding assays, respectively. Exposure of phosphatidylserine on the cell surface was analyzed using thrombin generation assay or by binding of a fluorescent dye-conjugated annexin V. 2',7'-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate was used to detect the generation of reactive oxygen species. Our data showed that HNE increased the procoagulant activity of unperturbed THP-1 cells that express traces of TF antigen, but had no effect on unperturbed endothelial cells that express no measurable TF antigen. HNE increased TF procoagulant activity but not TF antigen of both activated monocytic and endothelial cells. HNE treatment generated reactive oxygen species, activated p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase, and increased the exposure of phosphatidylserine at the outer leaflet in THP-1 cells. Treatment of THP-1 cells with an antioxidant, N-acetyl cysteine, suppressed the above HNE-induced responses and negated the HNE-mediated increase in TF activity. Blockade of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activation inhibited HNE-induced phosphatidylserine exposure and increased TF activity.
Conclusions: HNE increases TF coagulant activity in monocytic cells through a novel mechanism involving p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activation that leads to enhanced phosphatidylserine exposure at the cell surface.
Keywords: 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal; atherosclerosis; microparticles; oxidative stress; p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase; tissue factor.
Figures


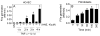
References
-
- Uchida K. Role of reactive aldehyde in cardiovascular diseases. Free Radic Biol Med. 2000;28:1685–1696. - PubMed
-
- Yin H, Xu L, Porter NA. Free radical lipid peroxidation: mechanisms and analysis. Chem Rev. 2011;111:5944–5972. - PubMed
-
- Strohmaier H, Hinghofer-Szalkay H, Schaur RJ. Detection of 4-hydroxynonenal (HNE) as a physiological component in human plasma. J Lipid Mediat Cell Signal. 1995;11:51–61. - PubMed
-
- Esterbauer H, Gebicki J, Puhl H, Jurgens G. The role of lipid peroxidation and antioxidants in oxidative modification of LDL. Free Radic Biol Med. 1992;13:341–390. - PubMed
-
- Usatyuk PV, Parinandi NL, Natarajan V. Redox regulation of 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal-mediated endothelial barrier dysfunction by focal adhesion, adherens, and tight junction proteins. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:35554–35566. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

