Notch1 promotes the pro-osteogenic response of human aortic valve interstitial cells via modulation of ERK1/2 and nuclear factor-κB activation
- PMID: 23640488
- PMCID: PMC3778193
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.112.300912
Notch1 promotes the pro-osteogenic response of human aortic valve interstitial cells via modulation of ERK1/2 and nuclear factor-κB activation
Abstract
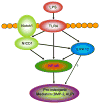
Objective: Calcific aortic valve disease is a leading cardiovascular disease in the elderly, and progressive calcification results in the failure of valvular function. Aortic valve interstitial cells (AVICs) from stenotic valves express higher levels of bone morphogenetic protein-2 in response to Toll-like receptor 4 stimulation. We recently found that Toll-like receptor 4 interacts with Notch1 in human AVICs. This study tests the hypothesis that Notch1 promotes the pro-osteogenic response of human AVICs.
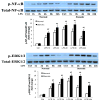
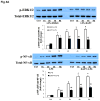
Approach and results: AVICs isolated from diseased human valves expressed higher levels of bone morphogenetic protein-2 and alkaline phosphatase after lipopolysaccharide stimulation. The augmented pro-osteogenic response is associated with elevated cellular levels of Notch1 and enhanced Notch1 cleavage in response to lipopolysaccharide stimulation. Inhibition or silencing of Notch1 suppressed the pro-osteogenic response in diseased cells, and the Notch 1 ligand, Jagged1, enhanced the response in AVICs isolated from normal human valves. Interestingly, extracellular signal-regulated protein kinases 1/2 (ERK1/2) and nuclear factor-κB phosphorylation induced by lipopolysaccharide was markedly reduced by inhibition or silencing of Notch1 and enhanced by Jagged1. Inhibition of ERK1/2 or nuclear factor-κB also reduced bone morphogenetic protein-2 and alkaline phosphatase expression induced by lipopolysaccharide.
Conclusions: Notch1 mediates the pro-osteogenic response to Toll-like receptor 4 stimulation in human AVICs. Elevated Notch1 levels and enhanced Notch1 activation play a major role in augmentation of the pro-osteogenic response of AVICs of stenotic valves through modulation of ERK1/2 and nuclear factor-κB activation. These pathways could be potential therapeutic targets for prevention of the progression of calcific aortic valve disease.
Keywords: Notch1; Toll-like receptor 4; aortic valve; pro-osteogenic proteins; signal transduction.
Figures











Similar articles
-
Augmented osteogenic responses in human aortic valve cells exposed to oxLDL and TLR4 agonist: a mechanistic role of Notch1 and NF-κB interaction.PLoS One. 2014 May 8;9(5):e95400. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0095400. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24810405 Free PMC article.
-
Biglycan induces the expression of osteogenic factors in human aortic valve interstitial cells via Toll-like receptor-2.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2012 Nov;32(11):2711-20. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.112.300116. Epub 2012 Sep 13. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2012. PMID: 22982459 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-talk between the Toll-like receptor 4 and Notch1 pathways augments the inflammatory response in the interstitial cells of stenotic human aortic valves.Circulation. 2012 Sep 11;126(11 Suppl 1):S222-30. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.083675. Circulation. 2012. PMID: 22965987 Free PMC article.
-
Lipoprotein(a) as Orchestrator of Calcific Aortic Valve Stenosis.Biomolecules. 2019 Nov 21;9(12):760. doi: 10.3390/biom9120760. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 31766423 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Macrophages in Calcific Aortic Valve Disease: Paracrine and Juxtacrine Disease Drivers.Biomolecules. 2024 Dec 2;14(12):1547. doi: 10.3390/biom14121547. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39766254 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Midkine Prevents Calcification of Aortic Valve Interstitial Cells via Intercellular Crosstalk.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Dec 15;9:794058. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.794058. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34977035 Free PMC article.
-
TLR4 Stimulation Promotes Human AVIC Fibrogenic Activity through Upregulation of Neurotrophin 3 Production.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 14;21(4):1276. doi: 10.3390/ijms21041276. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32074942 Free PMC article.
-
Thrombospondin-1 Silencing Ameliorates Osteoblastic Differentiation of Aortic Valve Interstitial Cells via Inhibiting Nuclear Factor-κB Pathway.Cardiovasc Ther. 2025 Apr 7;2025:3845211. doi: 10.1155/cdr/3845211. eCollection 2025. Cardiovasc Ther. 2025. PMID: 40231210 Free PMC article.
-
Parathyroid hormone promotes osteoblastic differentiation of endothelial cells via the extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase 1/2 and nuclear factor-κB signaling pathways.Exp Ther Med. 2018 Feb;15(2):1754-1760. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.5545. Epub 2017 Nov 23. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 29434762 Free PMC article.
-
Age related extracellular matrix and interstitial cell phenotype in pulmonary valves.Sci Rep. 2020 Dec 7;10(1):21338. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-78507-8. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33288823 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mohler ER, 3rd, Gannon F, Reynolds C, Zimmerman R, Keane MG, Kaplan FS. Bone formation and inflammation in cardiac valves. Circulation. 2001;103:1522–1528. - PubMed
-
- Rajamannan NM, Evans FJ, Aikawa E, Grande-Allen KJ, Demer LL, Heistad DD, Simmons CA, Masters KS, Mathieu P, O’Brien KD, Schoen FJ, Towler DA, Yoganathan AP, Otto CM. Calcific aortic valve disease: not simply a degenerative process: A review and agenda for research from the National Heart and Lung and Blood Institute Aortic Stenosis Working Group. Executive summary: Calcific aortic valve disease-2011 update. Circulation. 2011;124:1783–1791. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Osman L, Yacoub MH, Latif N, Amrani M, Chester AH. Role of human valve interstitial cells in valve calcification and their response to atorvastatin. Circulation. 2006;114:I547–552. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

