Diabetes and vascular disease: pathophysiology, clinical consequences, and medical therapy: part I
- PMID: 23641007
- PMCID: PMC3743069
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/eht149
Diabetes and vascular disease: pathophysiology, clinical consequences, and medical therapy: part I
Abstract
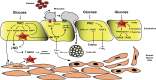
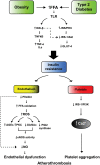
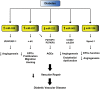
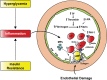
Hyperglycemia and insulin resistance are key players in the development of atherosclerosis and its complications. A large body of evidence suggest that metabolic abnormalities cause overproduction of reactive oxygen species (ROS). In turn, ROS, via endothelial dysfunction and inflammation, play a major role in precipitating diabetic vascular disease. A better understanding of ROS-generating pathways may provide the basis to develop novel therapeutic strategies against vascular complications in this setting. Part I of this review will focus on the most current advances in the pathophysiological mechanisms of vascular disease: (i) emerging role of endothelium in obesity-induced insulin resistance; (ii) hyperglycemia-dependent microRNAs deregulation and impairment of vascular repair capacities; (iii) alterations of coagulation, platelet reactivity, and microparticle release; (iv) epigenetic-driven transcription of ROS-generating and proinflammatory genes. Taken together these novel insights point to the development of mechanism-based therapeutic strategies as a promising option to prevent cardiovascular complications in diabetes.
Keywords: Diabetes; Pathophysiology; Vascular disease.
Figures
References
-
- Wild S, Roglic G, Green A, Sicree R, King H. Global prevalence of diabetes: estimates for the year 2000 and projections for 2030. Diabetes Care. 2004;27:1047–1053. - PubMed
-
- Report of the expert committee on the diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2003;26(Suppl 1):S5–S20. - PubMed
-
- DeFronzo RA, Ferrannini E. Insulin resistance. A multifaceted syndrome responsible for NIDDM, obesity, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Diabetes Care. 1991;14:173–194. - PubMed
-
- Wei M, Gaskill SP, Haffner SM, Stern MP. Effects of diabetes and level of glycemia on all-cause and cardiovascular mortality. The San Antonio Heart Study. Diabetes Care. 1998;21:1167–1172. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

