Meta-analysis of olfactory function in schizophrenia, first-degree family members, and youths at-risk for psychosis
- PMID: 23641047
- PMCID: PMC3885295
- DOI: 10.1093/schbul/sbt049
Meta-analysis of olfactory function in schizophrenia, first-degree family members, and youths at-risk for psychosis
Abstract
Background: Previous research has provided compelling support for olfactory dysfunction in schizophrenia patients, their first-degree relatives, and youth at-risk for psychosis. A previous meta-analysis revealed large effect sizes across olfactory tasks but was limited to 2 olfactory tasks and did not examine moderator variables. Thus, the current meta-analysis was undertaken to incorporate additional studies, risk cohorts, olfactory test domains, and moderator variable analyses.
Method: A meta-analysis was conducted on 67 publications examining olfactory function in schizophrenia patients and 15 publications examining olfactory functioning in youth at-risk for psychosis, first-degree relatives of schizophrenia patients, and individuals with schizotypy.
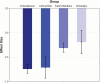
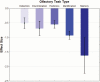
Results: Results revealed medium-to-large olfactory deficits in schizophrenia patients though significant heterogeneity was evident. Several variables moderated overall study effects. At-risk youths similarly demonstrated medium-to-large effect sizes, whereas first-degree relatives and individuals with schizotypy showed small effects.
Conclusions: Findings suggest robust olfactory deficits in schizophrenia and at-risk youths. In schizophrenia, several variables had significant impact on these deficits and warrant consideration in prospective studies. Our findings also indicate that olfactory measures may be a useful marker of schizophrenia risk status.
Keywords: olfaction; psychosis; schizophrenia prodrome; schizotypy; smell.
Figures
References
-
- Moberg PJ, Agrin R, Gur RE, Gur RC, Turetsky BI, Doty RL. Olfactory dysfunction in schizophrenia: a qualitative and quantitative review. Neuropsychopharmacology. 1999;21:325–340 - PubMed
-
- Brewer WJ, Pantelis C, Anderson V, et al. Stability of olfactory identification deficits in neuroleptic-naive patients with first-episode psychosis. Am J Psychiatry. 2001;158:107–115 - PubMed
-
- Moberg PJ, Doty RL, Turetsky BI, et al. Olfactory identification deficits in schizophrenia: correlation with duration of illness. Am J Psychiatry. 1997; 154: 1016–1018 - PubMed
-
- Rupp CI, Fleischhacker WW, Kemmler G, et al. Various bilateral olfactory deficits in male patients with schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull. 2005;31:155–165 - PubMed
-
- Wu J, Buchsbaum MS, Moy K, et al. Olfactory memory in unmedicated schizophrenics. Schizophr Res. 1993; 9: 41–47 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical