Direct binding of TUBB3 with DCC couples netrin-1 signaling to intracellular microtubule dynamics in axon outgrowth and guidance
- PMID: 23641072
- PMCID: PMC3711200
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.122184
Direct binding of TUBB3 with DCC couples netrin-1 signaling to intracellular microtubule dynamics in axon outgrowth and guidance
Abstract
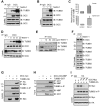
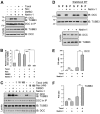
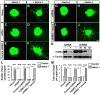
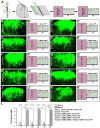
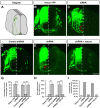
The coupling of axon guidance cues, such as netrin-1, to microtubule (MT) dynamics is essential for growth cone navigation in the developing nervous system. However, whether axon guidance signaling regulates MT dynamics directly or indirectly is unclear. Here, we report that TUBB3, the most dynamic β-tubulin isoform in neurons, directly interacts with the netrin receptor DCC, and that netrin-1 induces this interaction in primary neurons. TUBB3 colocalizes with DCC in the growth cones of primary neurons and MT dynamics is required for netrin-1-promoted association of TUBB3 with DCC. Netrin-1 not only increases co-sedimentation of DCC with polymerized MT, but also promotes MT dynamics in the growth cone. Knocking down TUBB3 inhibits netrin-1-induced MT dynamics, axon outgrowth and attraction in vitro and causes defects in commissural axon projection in the embryo. These results indicate that TUBB3 directly links netrin signaling pathways to MT dynamics and plays an important role in guiding commissural axons in vivo.
Keywords: Axon guidance; DCC; Microtubule dynamics; Netrin; Signal transduction; TUBB3.
Figures



References
-
- Alcántara S., Ruiz M., De Castro F., Soriano E., Sotelo C. (2000). Netrin 1 acts as an attractive or as a repulsive cue for distinct migrating neurons during the development of the cerebellar system. Development 127, 1359–1372 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

