YB-1 is a Transcription/Translation Factor that Orchestrates the Oncogenome by Hardwiring Signal Transduction to Gene Expression
- PMID: 23641145
- PMCID: PMC3634714
YB-1 is a Transcription/Translation Factor that Orchestrates the Oncogenome by Hardwiring Signal Transduction to Gene Expression
Abstract
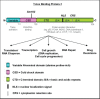
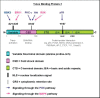
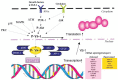
The Y-box Binding Protein-1 (YB-1) is a highly conserved oncogenic transcription/translation factor that is expressed in cancers affecting adults and children. It is now believed that YB-1 plays a causal role in the development of cancer given recent work showing that its expression drives the tumorigenesis in the mammary gland. In human breast cancers, YB-1 is associated with rapidly proliferating tumors that are highly aggressive. Moreover, expression of YB-1 promotes the growth of breast cancer cell lines both in monolayer and anchorage independent conditions. The involvement of YB-1 in breast cancer pathogenesis has made it a putative therapeutic target; however, the mechanism(s) that regulate YB-1 are poorly understood. This review first describes the oncogenic properties of YB-1 in cancer. It also highlights the importance of YB-1 in hardwiring signal transduction pathways to the regulation of genes involved in the development of cancer.
Keywords: YB-1; cancer; phosphorylation; signal transduction.
Figures
References
-
- Abbas T, White D, Hui L, et al. Inhibition of human p53 basal transcription by down-regulation of protein kinase Cdelta. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279(11):9970–7. - PubMed
-
- Ahmad S, Singh N, Glazer R. Role of Akt1 in 17β-estradiol- and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1)-dependent proliferation and prevention of apoptosis in MCF-7 breast carcinoma cells. Biochem Pharm. 1999;58:425–430. - PubMed
-
- Akita Y. Protein kinase C-epsilon (PKC-epsilon): its unique structure and function. J. Biochem, (Tokyo) 2002;132(6):847–52. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
