Natural radioactivity levels of some medicinal plants commonly used in Ghana
- PMID: 23641323
- PMCID: PMC3639363
- DOI: 10.1186/2193-1801-2-157
Natural radioactivity levels of some medicinal plants commonly used in Ghana
Abstract
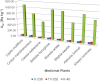
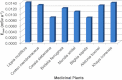
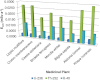
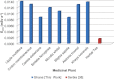
Natural radioactivity levels in some selected medicinal plants commonly used in Ghana from the Centre for Scientific Research into Plant Medicine were investigated to determine the activity concentration and the annual committed effective dose due to naturally occurring radionuclides of (238)U, (232)Th and (40)K. The activity concentration was determined using gamma-ray spectrometry. The results of the analysis indicated an average activity concentration of (238)U, (232)Th and (40)K in the medicinal plants to be 31.8±2.8 Bq kg(-1), 56.2±2.3 Bq kg(-1) and 839.8±11.9 Bq kg(-1) respectively. Khaya ivorensis recorded the highest activity concentration of (238)U and (232)Th while Lippia multiflora recorded the highest activity concentrations of (40)K. The total annual committed effective doses ranged from 0.026±0.001 to 0.042±0.002 mSv a(-1) with an average value of 0.035±0.001 mSv a(-1). The average annual committed effective dose due to ingestion of the natural radionuclides in the medicinal plant samples were far below the world average annual committed effective dose of 0.3 mSv a(-1) for ingestion of natural radionuclides provided in UNSCEAR 2000 report. Therefore, the radiological hazard associated with intake of the natural radionuclides in the medicinal plants is insignificant. The results provide baseline values which may be useful in establishing rules and regulations relating to radiation protection as well as developing standards and guidelines for the use of medicinal or herbal plants to the appropriate authorities.
Keywords: Annual committed effective dose; Gamma-ray spectrometry; Medicinal plants; Natural radioactivity.
Figures
References
-
- Abu-Khadra SA, Eissa HS. Natural radionuclides in different plants, together with their corresponding soils in Egypt at Inshas region and the area nearby, IX radiation physics & protection conference. National Network of Radiation Physics-Egyptian Atomic Energy Authority: Nasr city - Cairo; 2008. pp. 239–249.
-
- Adewumi AA. Assessment of norm-containing food crops/stuffs in OML 58 & OML 61 within the Niger delta region of Nigeria Proceedings of the 1st international technology, education and environment conference, African society for scientific research (ASSR) 2011. pp. 594–603.
-
- Potassume-40 Argonne national laboratory, EVS, human health fact sheet. 2005.
-
- Bhatti TM, Malik KA. Phosphate fertilizers a potential source for uranium recovery as by product, National institute for biotechnology and genetic engineering (NIBGE) Technical report no PAEC/NIBGE-2/1994: Faisalabad Pakistan; 1994.
-
- Brown K. Medicinal plants, indigenous medicine and conservation of biodiversity in Ghana. Norwich, UK: Centre for Social and Economic Research on Global Environment (CSERGE); 1992.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

