Estimation of the Serial Interval for Pandemic Influenza (pH1N1) in the Most Southern Province of Argentina
- PMID: 23641387
- PMCID: PMC3640778
Estimation of the Serial Interval for Pandemic Influenza (pH1N1) in the Most Southern Province of Argentina
Abstract
Background: A retrospective cohort study, in the context of household transmission, to estimate the serial interval (SI) of pH1N1 influenza in the island of Tierra del Fuego was carried out.
Methods: We collected data from the epidemiological surveillance system during disease outbreak in Ushuaia and Rio Grande, the two main cities of the southernmost province of Argentina. Only the records of patients and households with a positive result of RT-PCR assay for pH1N1 virus were used.
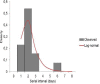
Results: A total of 283 laboratory confirmed cases were detected, from 550 samples analyzed. Hospitalizations were necessary in 13.8% of patients, yet no deaths were reported. Complete data of household contacts were available in 13 patients. We calculated an SI of 2.0 days (95% CI = 1.5 - 2.6 days), fitting to a log-normal distribution, the one that presented the best adjustment.
Conclusion: These results were consistent with estimates of SI calculated from Mexico, but lower than estimations from Canada, Germany and USA. We discuss these differences in relation to limitations of the current study design.
Keywords: Argentina; Epidemiologic models; H1N1 subtype; Influenza A Virus.
Figures
References
-
- Raffo L. Influenza A (H1N1) epidemic in Argentina. Experience in a National General Hospital (Hospital Nacional Alejandro Posadas) Medicina (B Aires) 2009;69(4):393–423. - PubMed
-
- Orellano PW, Grassi A, Reynoso JI, Palmieri A, Uez O, Carlino O. Impact of school closings on the influenza A (H1N1) outbreak in Tierra del Fuego, Argentina. Rev Panam Salud Publica. 2010;27(3):226–9. - PubMed
-
- Fine PE. The interval between successive cases of an infectious disease. Am J Epidemiol. 2003;158(11):1039–47. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization WHO CDC protocol of realtime RT-PCR for influenza A (H1N1) 2009. Available from: http://www.who.int/csr/resources/publications/swineflu/CDCRealtimeRTPCR_....
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources