Simple method to enhance the photostability of the fluorescence reporter R6G for prolonged single-molecule studies
- PMID: 23641719
- PMCID: PMC3723744
- DOI: 10.1021/jp4003643
Simple method to enhance the photostability of the fluorescence reporter R6G for prolonged single-molecule studies
Abstract
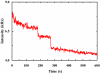
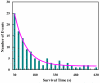
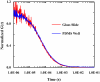
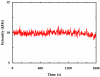
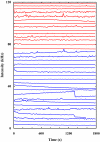
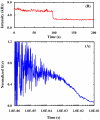
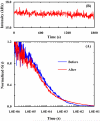
For fluorescence-based single-molecule studies, photobleaching of the dye reporter often limits the time window over which individual molecules can be followed. As such, many strategies, for example, using a cocktail of chemical reagents, have been developed to decrease the rate of photobleaching. Herein, we introduce a new and highly effective method to enhance the photostability of one of the commonly used fluorescent dyes, rhodamine 6G (R6G). We show that micrometer-sized polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) wells, when the PDMS surface is properly treated, not only provide a confined environment for single-molecule detection but can also significantly increase the survival time of individual R6G molecules before photobleaching. Moreover, our results suggest, consistent with several previous studies, that R6G photobleaching involves a radical state.
Figures


References
-
- Joo C, Balci H, Ishitsuka Y, Buranachai C, Ha T. Advances in Single-Molecule Fluorescence Methods for Molecular Biology. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2008;77:51–76. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

