Rifampicin-warfarin interaction leading to macroscopic hematuria: a case report and review of the literature
- PMID: 23641931
- PMCID: PMC3653703
- DOI: 10.1186/2050-6511-14-27
Rifampicin-warfarin interaction leading to macroscopic hematuria: a case report and review of the literature
Abstract
Background: Rifampicin remains one of the first-line drugs used in tuberculosis therapy. This drug's potential to induce the hepatic cytochrome P450 oxidative enzyme system increases the risk of drug-drug interactions. Thus, although the presence of comorbidities typically necessitates the use of multiple drugs, the co-administration of rifampicin and warfarin may lead to adverse drug events. We report a bleeding episode after termination of the co-administration of rifampicin and warfarin and detail the challenges related to international normalized ratio (INR) monitoring.
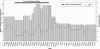
Case presentation: A 59-year-old Brazilian woman chronically treated with warfarin for atrial fibrillation (therapeutic INR range: 2.0-3.0) was referred to a multidisciplinary anticoagulation clinic at a university hospital. She showed anticoagulation resistance at the beginning of rifampicin therapy, as demonstrated by repeated subtherapeutic INR values. Three months of sequential increases in the warfarin dosage were necessary to reach a therapeutic INR, and frequent visits to the anticoagulation clinic were needed to educate the patient about her pharmacotherapy and to perform the warfarin dosage adjustments. The warfarin dosage also had to be doubled at the beginning of rifampicin therapy. However, four weeks after rifampicin discontinuation, an excessively high INR was observed (7.22), with three-day macroscopic hematuria and the need for an immediate reduction in the warfarin dosage. A therapeutic and stable INR was eventually attained at 50% of the warfarin dosage used by the patient during tuberculosis therapy.
Conclusions: The present case exemplifies the influence of rifampicin therapy on warfarin dosage requirements and the increased risk of bleeding after rifampicin discontinuation. Additionally, this case highlights the need for warfarin weekly monitoring after stopping rifampicin until the maintenance dose of warfarin has decreased to the amount administered before rifampicin use. In particular, patients with cardiovascular diseases and active tuberculosis represent a group with a substantial risk of drug-drug interactions. Learning how to predict and monitor drug-drug interactions may help reduce the incidence of clinically significant adverse drug events.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Difficulties in anticoagulation management during coadministration of warfarin and rifampin.Pharmacotherapy. 2001 Oct;21(10):1240-6. doi: 10.1592/phco.21.15.1240.33897. Pharmacotherapy. 2001. PMID: 11601670
-
Describing the profile of patients on concurrent rifampin and warfarin therapy in western Kenya: a case series.Drugs R D. 2013 Sep;13(3):191-7. doi: 10.1007/s40268-013-0023-7. Drugs R D. 2013. PMID: 23982688 Free PMC article.
-
Delayed de-induction of CYP2C9 compared to CYP3A after discontinuation of rifampicin: Report of two cases .Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2017 May;55(5):449-452. doi: 10.5414/CP202764. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2017. PMID: 28157069
-
Update on the interaction of rifampin and warfarin.Prog Cardiovasc Nurs. 2007 Spring;22(2):97-100. doi: 10.1111/j.0889-7204.2007.05782.x. Prog Cardiovasc Nurs. 2007. PMID: 17541320 Review.
-
Potential glucosamine-warfarin interaction resulting in increased international normalized ratio: case report and review of the literature and MedWatch database.Pharmacotherapy. 2008 Apr;28(4):540-8. doi: 10.1592/phco.28.4.540. Pharmacotherapy. 2008. PMID: 18363538 Review.
Cited by
-
A cross-sectional evaluation of five warfarin anticoagulation services in Uganda and South Africa.PLoS One. 2020 Jan 29;15(1):e0227458. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0227458. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 31995565 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and validation of NETs-related biomarkers in active tuberculosis through bioinformatics analysis and machine learning algorithms.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 18;16:1599667. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1599667. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40607433 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of rifampicin on anticoagulation of warfarin: A case report.World J Clin Cases. 2021 Feb 16;9(5):1087-1095. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i5.1087. World J Clin Cases. 2021. PMID: 33644171 Free PMC article.
-
Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage Caused by Warfarin after Rifampicin Discontinuation.Case Rep Med. 2019 Jan 23;2019:4917856. doi: 10.1155/2019/4917856. eCollection 2019. Case Rep Med. 2019. PMID: 30809261 Free PMC article.
-
Oral anticoagulants and concurrent rifampin administration in tuberculosis patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2023 Apr 4;23(1):182. doi: 10.1186/s12872-023-03212-z. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2023. PMID: 37016321 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Toman’s tuberculosis: case detection, treatment, and monitoring. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2004.
-
- Manosuthi W, Tantanathip P, Prasithisirikul W, Likanonsakul S, Sungkanuparph S. Durability of stavudine, lamivudine and nevirapine among advanced HIV-1 infected patients with/without prior co-administration of rifampicin: a 144-week prospective study. BMC Infect Dis. 2008;8:136. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-8-136. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

