Multiscale computational models of complex biological systems
- PMID: 23642247
- PMCID: PMC3970111
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-bioeng-071811-150104
Multiscale computational models of complex biological systems
Abstract
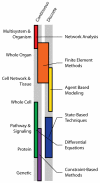
Integration of data across spatial, temporal, and functional scales is a primary focus of biomedical engineering efforts. The advent of powerful computing platforms, coupled with quantitative data from high-throughput experimental methodologies, has allowed multiscale modeling to expand as a means to more comprehensively investigate biological phenomena in experimentally relevant ways. This review aims to highlight recently published multiscale models of biological systems, using their successes to propose the best practices for future model development. We demonstrate that coupling continuous and discrete systems best captures biological information across spatial scales by selecting modeling techniques that are suited to the task. Further, we suggest how to leverage these multiscale models to gain insight into biological systems using quantitative biomedical engineering methods to analyze data in nonintuitive ways. These topics are discussed with a focus on the future of the field, current challenges encountered, and opportunities yet to be realized.
Figures


References
-
- Frank RN. Diabetic retinopathy. The New England journal of medicine. 2004;350:48–58. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

