Small-molecule pyrimidine inhibitors of the cdc2-like (Clk) and dual specificity tyrosine phosphorylation-regulated (Dyrk) kinases: development of chemical probe ML315
- PMID: 23642479
- PMCID: PMC3664191
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2013.02.096
Small-molecule pyrimidine inhibitors of the cdc2-like (Clk) and dual specificity tyrosine phosphorylation-regulated (Dyrk) kinases: development of chemical probe ML315
Abstract
Substituted pyrimidine inhibitors of the Clk and Dyrk kinases have been developed, exploring structure-activity relationships around four different chemotypes. The most potent compounds have low-nanomolar inhibitory activity against Clk1, Clk2, Clk4, Dyrk1A and Dyrk1B. Kinome scans with 442 kinases using agents representing three of the chemotypes show these inhibitors to be highly selective for the Clk and Dyrk families. Further off-target pharmacological evaluation with ML315, the most selective agent, supports this conclusion.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
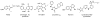
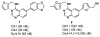
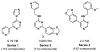




Similar articles
-
Potent and selective small molecule inhibitors of specific isoforms of Cdc2-like kinases (Clk) and dual specificity tyrosine-phosphorylation-regulated kinases (Dyrk).Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2011 May 15;21(10):3152-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2011.02.114. Epub 2011 Mar 4. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2011. PMID: 21450467 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of selective inhibitors of cdc2-like kinases 1 and 4 (Clk1, Clk4).2012 Apr 16 [updated 2013 May 8]. In: Probe Reports from the NIH Molecular Libraries Program [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2010–. 2012 Apr 16 [updated 2013 May 8]. In: Probe Reports from the NIH Molecular Libraries Program [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2010–. PMID: 23926621 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Design and synthesis of a library of lead-like 2,4-bisheterocyclic substituted thiophenes as selective Dyrk/Clk inhibitors.PLoS One. 2014 Mar 27;9(3):e87851. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087851. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24676346 Free PMC article.
-
Human CDC2-like kinase 1 (CLK1): a novel target for Alzheimer's disease.Curr Drug Targets. 2014 May;15(5):539-50. doi: 10.2174/1389450115666140226112321. Curr Drug Targets. 2014. PMID: 24568585 Review.
-
Marine-Derived 2-Aminoimidazolone Alkaloids. Leucettamine B-Related Polyandrocarpamines Inhibit Mammalian and Protozoan DYRK & CLK Kinases.Mar Drugs. 2017 Oct 17;15(10):316. doi: 10.3390/md15100316. Mar Drugs. 2017. PMID: 29039762 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of DYRK1A Stimulates Human β-Cell Proliferation.Diabetes. 2016 Jun;65(6):1660-71. doi: 10.2337/db15-1127. Epub 2016 Mar 7. Diabetes. 2016. PMID: 26953159 Free PMC article.
-
Cdc2-like kinases: structure, biological function, and therapeutic targets for diseases.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023 Apr 7;8(1):148. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01409-4. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023. PMID: 37029108 Free PMC article. Review.
-
5-Methoxybenzothiophene-2-Carboxamides as Inhibitors of Clk1/4: Optimization of Selectivity and Cellular Potency.Molecules. 2021 Feb 13;26(4):1001. doi: 10.3390/molecules26041001. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33668683 Free PMC article.
-
The Tumor Suppressor NKX3.1 Is Targeted for Degradation by DYRK1B Kinase.Mol Cancer Res. 2015 May;13(5):913-22. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-14-0680. Epub 2015 Mar 16. Mol Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 25777618 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and Biological Evaluation of a Novel CLK4 Inhibitor Targeting Alternative Splicing in Pancreatic Cancer Using Structure-Based Virtual Screening.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025 May;12(19):e2416323. doi: 10.1002/advs.202416323. Epub 2025 Mar 24. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025. PMID: 40126184 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

