Chromosomal instability triggered by Rrm2b loss leads to IL-6 secretion and plasmacytic neoplasms
- PMID: 23643536
- PMCID: PMC3672259
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2013.03.040
Chromosomal instability triggered by Rrm2b loss leads to IL-6 secretion and plasmacytic neoplasms
Abstract
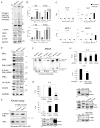
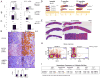
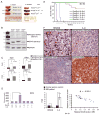
Chronic inflammation has a tight cause-and-effect relationship with DNA damage by inflicting tissue damage and increasing cancer risk. Rrm2b, a key enzyme in de novo deoxyribonucleotide synthesis, is involved in DNA damage repair, but its role in cancer development has yet to be demonstrated. In this work, Rrm2b gene loss led to severe numerical and structural chromosome abnormalities that caused ATM activation, inducing p-Ser85 IKKγ/NEMO and IκB kinase (IKK). NF-κB consequently induced by IKK triggered sustained IL-6 expression that constitutively activated STAT3 in Rrm2b-deficient cells. High plasma interleukin-6 (IL-6) and associated hematologic disorders were observed in Rrm2b-/- mice, and 30%-40% of aged Rrm2b heterozygous knockout mice developed plasma cell neoplasms and suffered from progressive splenomegaly and ascites. The genetic ablation of IL-6 suppressed STAT3 induction and delayed disease onset in Rrm2b-/- mice, extending their lifespan. Thus, Rrm2b plays a crucial role in maintaining chromosomal stability and preventing chronic-inflammation-associated tumorigenesis.
Copyright © 2013 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Bourdon A, Minai L, Serre V, Jais JP, Sarzi E, Aubert S, Chretien D, de Lonlay P, Paquis-Flucklinger V, Arakawa H, et al. Mutation of RRM2B, encoding p53-controlled ribonucleotide reductase (p53R2), causes severe mitochondrial DNA depletion. Nature genetics. 2007;39:776–780. - PubMed
-
- Chang L, Zhou B, Hu S, Guo R, Liu X, Jones SN, Yen Y. ATM-mediated serine 72 phosphorylation stabilizes ribonucleotide reductase small subunit p53R2 protein against MDM2 to DNA damage. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2008;105:18519–18524. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Grivennikov S, Karin M. Autocrine IL-6 signaling: a key event in tumorigenesis? Cancer Cell. 2008;13:7–9. - PubMed
-
- Kimura T, Takeda S, Sagiya Y, Gotoh M, Nakamura Y, Arakawa H. Impaired function of p53R2 in Rrm2b-null mice causes severe renal failure through attenuation of dNTP pools. Nature genetics. 2003;34:440–445. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

