Efficacy and durability of radiofrequency ablation for Barrett's Esophagus: systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 23644385
- PMCID: PMC3870150
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2013.03.039
Efficacy and durability of radiofrequency ablation for Barrett's Esophagus: systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background & aims: In patients with Barrett's esophagus (BE), radiofrequency ablation (RFA) safely and effectively eradicates dysplasia and intestinal metaplasia. We aimed to determine the efficacy and durability of RFA for patients with dysplastic and nondysplastic BE.
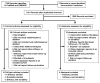
Methods: We performed a systematic review and meta-analysis of studies identified in PubMed and EMBASE that reported the proportion of patients treated with RFA who had complete eradication of dysplasia (CE-D) and intestinal metaplasia (CE-IM), and the proportion of patients with recurrent IM after successful treatment. Pooled estimates of CE-D, CE-IM, IM recurrence, and adverse events were calculated.
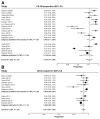
Results: We identified 18 studies of 3802 patients reporting efficacy and 6 studies of 540 patients reporting durability. Ten were prospective cohort studies, 9 were retrospective cohort studies, and 1 was a randomized trial. CE-IM was achieved in 78% of patients (95% confidence interval [CI], 70%-86%) and CE-D was achieved in 91% (95% CI, 87%-95%). After eradication, IM recurred in 13% (95% CI, 9%-18%). Progression to cancer occurred in 0.2% of patients during treatment and in 0.7% of those after CE-IM. Esophageal stricture was the most common adverse event and was reported in 5% of patients (95% CI, 3%-7%). Confidence in most summary estimates was limited by a high degree of heterogeneity, which did not appear to be caused by single outlier studies.
Conclusions: Treatment of BE with RFA results in CE-D and CE-IM in a high proportion of patients, with few recurrences of IM after treatment and a low rate of adverse events. Despite the large amount of study heterogeneity, these data provide additional information for patients and providers to make informed treatment decisions.
Keywords: AIM; Ablation of Intestinal Metaplasia; BE; Barrett's esophagus; CE-D; CE-IM; CI; EAC; EMR; Endoscopy; Esophageal Cancer; Gastroesophageal Reflux; HGD; IM; IMC; LGD; NDBE; Prevention; RCT; RFA; RR; complete eradication of dysplasia; complete eradication of intestinal metaplasia; confidence interval; endoscopic mucosal resection; esophageal adenocarcinoma; high-grade dysplasia; intestinal metaplasia; intramucosal carcinoma; low-grade dysplasia; nondysplastic Barrett's esophagus; radiofrequency ablation; randomized controlled trial; risk ratio.
Copyright © 2013 AGA Institute. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest
This author discloses the following: Dr Shaheen has received research grants from BARRX Medical, Oncoscope, CSA Medical, Takeda, and AstraZeneca; and is a consultant for CSA Medical, Astra-Zeneca, Takeda, Oncoscope, and NeoGenomics. The remaining authors disclose no conflicts.
Figures
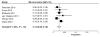
Comment in
-
Radiofrequency ablation for Barrett's esophagus, for whom and by whom?Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013 Oct;11(10):1256-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2013.06.014. Epub 2013 Jun 28. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013. PMID: 23811256 No abstract available.
References
-
- Spechler SJ, Sharma P, Souza RF, et al. American Gastroenterological Association medical position statement on the management of Barrett’s esophagus. Gastroenterology. 2011;140:1084–1091. - PubMed
-
- Ronkainen J, Aro P, Storskrubb T, et al. Prevalence of Barrett’s esophagus in the general population: an endoscopic study. Gastroenterology. 2005;129:1825–1831. - PubMed
-
- Hvid-Jensen F, Pedersen L, Drewes AM, et al. Incidence of adenocarcinoma among patients with Barrett’s esophagus. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:1375–1383. - PubMed
-
- Sharma VK, Wang KK, Overholt BF, et al. Balloon-based, circumferential, endoscopic radiofrequency ablation of Barrett’s esophagus: 1-year follow-up of 100 patients. Gastrointest Endosc. 2007;65:185–195. - PubMed
-
- Overholt BF, Panjehpour M, Haydek JM. Photodynamic therapy for Barrett’s esophagus: follow-up in 100 patients. Gastrointest Endosc. 1999;49:1–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

