Multifaceted role of EZH2 in breast and prostate tumorigenesis: epigenetics and beyond
- PMID: 23644490
- PMCID: PMC3741216
- DOI: 10.4161/epi.24532
Multifaceted role of EZH2 in breast and prostate tumorigenesis: epigenetics and beyond
Abstract
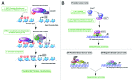
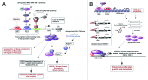
Overexpression of EZH2 and other PRC2 subunits, such as SUZ12, is associated with tumor progression and poor prognosis in several human malignancies. Nevertheless, the underlying mechanisms driving aberrant EZH2 expression are poorly understood. This review provides molecular insights into the essential role of EZH2 in breast and prostate tumorigenesis. We addressed the current understanding on the oncogenic role of EZH2, with an emphasis on: (1) the less known PRC2-independent role of EZH2 in gene activation, in addition to its canonical role in transcriptional silencing as a histone methyltransferase catalyzing the trimethylation of histone H3 at lysine 27; (2) causes and consequences of its deregulation in tumor cells and; (3) collaboration of EZH2 with other epigenetic and hormone receptor-mediated oncogenic signaling pathways. We also summarize how EZH2 has emerged as a promising therapeutic target in hormone-refractory cancers and the prospects for integrating EZH2 blockade with available pharmacological inhibitors.
Keywords: EZH2; H3K27 trimethylation; PRC2 complex; androgen receptor; breast cancer; estrogen receptor; prostate cancer.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
