β1 integrin targeting potentiates antiangiogenic therapy and inhibits the growth of bevacizumab-resistant glioblastoma
- PMID: 23644530
- PMCID: PMC4040366
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-0011
β1 integrin targeting potentiates antiangiogenic therapy and inhibits the growth of bevacizumab-resistant glioblastoma
Abstract
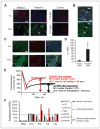
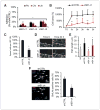
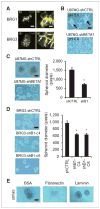
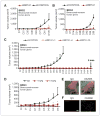
Antiangiogenic therapies like bevacizumab offer promise for cancer treatment, but acquired resistance, which often includes an aggressive mesenchymal phenotype, can limit the use of these agents. Upregulation of β1 integrin (ITGB1) occurs in some bevacizumab-resistant glioblastomas (BRG) whereby, mediating tumor-microenvironment interactions, we hypothesized that it may mediate a mesenchymal-type resistance to antiangiogenic therapy. Immunostaining analyses of β1 integrin and its downstream effector kinase FAK revealed upregulation in 75% and 86% of BRGs, respectively, compared with pretreatment paired specimens. Furthermore, flow cytometry revealed eight-fold more β1 integrin in primary BRG cells compared with cells from bevacizumab-naïve glioblastomas (BNG). Fluorescence recovery after photobleaching of cells engineered to express a β1-GFP fusion protein indicated that the mobile β1 integrin fraction was doubled, and half-life of β1 integrin turnover in focal adhesions was reduced markedly in BRG cells compared with bevacizumab-responsive glioblastoma multiforme cells. Hypoxia, which was increased with acquisition of bevacizumab resistance, was associated with increased β1 integrin expression in cultured BNG cells. BRGs displayed an aggressive mesenchymal-like phenotype in vitro. We found that growth of BRG xenograft tumors was attenuated by the β1 antibody, OS2966, allowing a 20-fold dose reduction of bevacizumab per cycle in this model. Intracranial delivery of OS2966 through osmotic pumps over 28 days increased tumor cell apoptosis, decreased tumor cell invasiveness, and blunted the mesenchymal morphology of tumor cells. We concluded that β1 integrin upregulation in BRGs likely reflects an onset of hypoxia caused by antiangiogenic therapy, and that β1 inhibition is well tolerated in vivo as a tractable strategy to disrupt resistance to this therapy.
©2013 AACR.
Conflict of interest statement
W. Shawn Carbonell is employed as a cofounder, President, and CEO, and has ownership interest (including patents) in OncoSynergy, Inc. C.C. Park has ownership interest (including patents) in Oncosynergy Ltd. M.K. Aghi is employed as a scientific advisory board member/shareholder, has ownership interest (including patents), and is a consultant/advisory board member of Oncosynergy. No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed by the other authors.
Figures

References
-
- Stupp R, Dietrich PY, Ostermann Kraljevic S, Pica A, Maillard I, Maeder P, et al. Promising survival for patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma multiforme treated with concomitant radiation plus temozolomide followed by adjuvant temozolomide. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20:1375–82. - PubMed
-
- Kienast Y, Winkler F. Therapy and prophylaxis of brain metastases. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2010;10:1763–77. - PubMed
-
- Vredenburgh JJ, Desjardins A, Herndon JE, II, Dowell JM, Reardon DA, Quinn JA, et al. Phase II trial of bevacizumab and irinotecan in recurrent malignant glioma. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:1253–9. - PubMed
-
- Gotzmann J, Mikula M, Eger A, Schulte-Hermann R, Foisner R, Beug H, et al. Molecular aspects of epithelial cell plasticity: implications for local tumor invasion and metastasis. Mutat Res. 2004;566:9–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

