Association between muscle strength and the cardiopulmonary status of individuals living with HIV/AIDS
- PMID: 23644856
- PMCID: PMC3611747
- DOI: 10.6061/clinics/2013(03)oa12
Association between muscle strength and the cardiopulmonary status of individuals living with HIV/AIDS
Abstract
Objective: The purpose of this study was to compare aerobic function [anaerobic threshold (%VO(2)-AT), respiratory compensation point (%VO(2)-RCP) and peak oxygen uptake (VO(2)peak)] between physically active patients with HIV/AIDS and matched controls and to examine associations between disease status, poor muscle strength, depression (as estimated by the profile of mood states questionnaire) and the aerobic performance of patients.
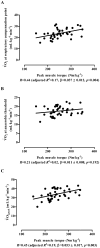
Methods: Progressive treadmill test data for %VO(2)-AT (V-slope method), RCP and (VO(2)peak) were compared between 39 male patients with HIV/AIDS (age 40.6 ± 1.4 years) and 28 male controls (age 44.4 ± 2.1 years) drawn from the same community and matched for habitual physical activity. Within-patient data were also examined in relation to CD4+ counts (nadir and current data) and peak isokinetic knee torque.
Results: AT, RCP and (VO(2)peak) values were generally similar for patients and controls.Within the patient sample, binary classification suggested that AT, RCP and (VO(2)peak) values were not associated with either the nadir or current CD4+ count, but treadmill test variables were positively associated with peak isokinetic knee torque.
Conclusion: The aerobic performance of physically active patients with HIV/AIDS is generally well conserved. Nevertheless, poor muscle strength is observed in some HIV/AIDS patients, which is associated with lower anaerobic power and (VO(2)peak), suggesting the possibility of enhancing the aerobic performance of patients with weak muscles through appropriate muscle-strengthening activities.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported.
Figures
References
-
- Raso V, Senf ME, Casseb JSR, Duarte AJS, Greve JMD. American College of Sports Medicine Annual Meeting. Vol. 42. Baltimore: Philadelphia: Med Sci Sports Exerc; Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; 2010. Muscle strength seems to predict immunological parameters in HIV-infected individuals; p. p. S258. v.
-
- Roubenoff R. Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome wasting, functional performance, and quality of life. Am J Manag Care. 2000;6(9):1003–16. - PubMed
-
- Das S, Shahmanesh M, Stolinski M, Shojaee-Moradie F, Jefferson W, Jackson NC, et al. In treatment-naïve and antiretroviral-treated subjects with HIV, reduced plasma adiponectin is associated with a reduced fractional clearance rate of VLDL, IDL and LDL apolipoprotein B-100. Diabetologia. 2006;49(3):538–42. - PubMed
-
- Grinspoon S, Carr A. Cardiovascular risk and body-fat abnormalities in HIV-infected adults. N Engl J Med. 2005;352(1):48–62. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials