What are the rates and causes of hospital readmission after total knee arthroplasty?
- PMID: 23645339
- PMCID: PMC3889434
- DOI: 10.1007/s11999-013-3030-7
What are the rates and causes of hospital readmission after total knee arthroplasty?
Abstract
Background: Total knee arthroplasty (TKA) and related interventions such as revision TKA and the treatment of infected TKAs are commonly performed procedures. Hospital readmission rates are used to measure hospital performance, but risk factors (both medical and surgical) for readmission after TKA, revision TKA, and treatment for the infected TKA have not been well characterized.
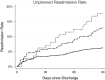
Questions/purposes: We measured (1) the unplanned hospital readmission rate in primary TKA and revision TKA, including antibiotic-spacer staged revision TKA to treat infection. We also evaluated (2) the medical and surgical causes of readmission and (3) risk factors associated with unplanned hospital readmission.
Methods: This retrospective cohort study included a total of 1408 patients (1032 primary TKAs, 262 revision TKAs, 113 revision of infected TKAs) from one institution. All hospital readmissions within 90 days of discharge were evaluated for timing and cause. Diagnoses at readmission were categorized as surgical or medical. Readmission risk was assessed using a Cox proportional hazards model that incorporated patient demographics and medical comorbidities.
Results: The unplanned readmission rate for the entire cohort was 4% at 30 days and 8% at 90 days. At 90 days postoperatively, revision of an infected TKA had the highest readmission rate, followed by revision TKA, with primary TKA having the lowest rate. Approximately three-fourths of readmissions were the result of surgical causes, mostly infection, arthrofibrosis, and cellulitis, whereas the remainder of readmissions were the result of medical causes. Procedure type (primary TKA versus revision TKA or staged treatment for infected TKA), hospital stay more than 5 days, discharge destination, and a fluid/electrolyte abnormality were each associated with risk of unplanned readmission.
Conclusions: Patients having revision TKA, whether for infection or other causes, are more likely to have an unplanned readmission to the hospital than are patients having primary TKA. When assessing hospital performance for TKA, it is important to distinguish among these surgical procedures.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical