Antagonistic basic helix-loop-helix/bZIP transcription factors form transcriptional modules that integrate light and reactive oxygen species signaling in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 23645630
- PMCID: PMC3694698
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.112.104869
Antagonistic basic helix-loop-helix/bZIP transcription factors form transcriptional modules that integrate light and reactive oxygen species signaling in Arabidopsis
Abstract
The critical developmental switch from heterotrophic to autotrophic growth of plants involves light signaling transduction and the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). ROS function as signaling molecules that regulate multiple developmental processes, including cell death. However, the relationship between light and ROS signaling remains unclear. Here, we identify transcriptional modules composed of the basic helix-loop-helix and bZIP transcription factors PHYTOCHROME-INTERACTING FACTOR1 (PIF1), PIF3, ELONGATED HYPOCOTYL5 (HY5), and HY5 HOMOLOGY (HYH) that bridge light and ROS signaling to regulate cell death and photooxidative response. We show that pif mutants release more singlet oxygen and exhibit more extensive cell death than the wild type during Arabidopsis thaliana deetiolation. Genome-wide expression profiling indicates that PIF1 represses numerous ROS and stress-related genes. Molecular and biochemical analyses reveal that PIF1/PIF3 and HY5/HYH physically interact and coordinately regulate the expression of five ROS-responsive genes by directly binding to their promoters. Furthermore, PIF1/PIF3 and HY5/HYH function antagonistically during the seedling greening process. In addition, phytochromes, cryptochromes, and CONSTITUTIVE PHOTOMORPHOGENIC1 act upstream to regulate ROS signaling. Together, this study reveals that the PIF1/PIF3-HY5/HYH transcriptional modules mediate crosstalk between light and ROS signaling and sheds light on a new mechanism by which plants adapt to the light environments.
Figures
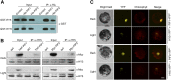
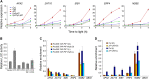
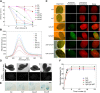
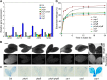

Comment in
-
Frenemies: antagonistic bHLH/bZIP transcription factors integrate light and reactive oxygen species signaling in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell. 2013 May;25(5):1483. doi: 10.1105/tpc.113.250510. Epub 2013 May 7. Plant Cell. 2013. PMID: 23653470 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Achard P., Renou J.-P., Berthomé R., Harberd N.P., Genschik P. (2008). Plant DELLAs restrain growth and promote survival of adversity by reducing the levels of reactive oxygen species. Curr. Biol. 18: 656–660 - PubMed
-
- Alabadí D., Blázquez M.A. (2009). Molecular interactions between light and hormone signaling to control plant growth. Plant Mol. Biol. 69: 409–417 - PubMed
-
- Al-Sady B., Ni W., Kircher S., Schäfer E., Quail P.H. (2006). Photoactivated phytochrome induces rapid PIF3 phosphorylation prior to proteasome-mediated degradation. Mol. Cell 23: 439–446 - PubMed
-
- Apel K., Hirt H.R. (2004). Reactive oxygen species: Metabolism, oxidative stress, and signal transduction. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 55: 373–399 - PubMed
-
- Bauer D., Viczián A., Kircher S., Nobis T., Nitschke R., Kunkel T., Panigrahi K.C., Adám E., Fejes E., Schäfer E., Nagy F. (2004). Constitutive photomorphogenesis 1 and multiple photoreceptors control degradation of phytochrome interacting factor 3, a transcription factor required for light signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 16: 1433–1445 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

