A self-defeating anabolic program leads to β-cell apoptosis in endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced diabetes via regulation of amino acid flux
- PMID: 23645676
- PMCID: PMC3682525
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.466920
A self-defeating anabolic program leads to β-cell apoptosis in endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced diabetes via regulation of amino acid flux
Abstract
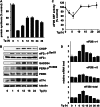
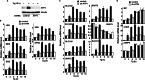
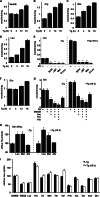
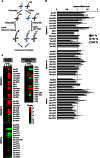
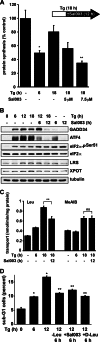
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress-induced responses are associated with the loss of insulin-producing β-cells in type 2 diabetes mellitus. β-Cell survival during ER stress is believed to depend on decreased protein synthesis rates that are mediated via phosphorylation of the translation initiation factor eIF2α. It is reported here that chronic ER stress correlated with increased islet protein synthesis and apoptosis in β-cells in vivo. Paradoxically, chronic ER stress in β-cells induced an anabolic transcription program to overcome translational repression by eIF2α phosphorylation. This program included expression of amino acid transporter and aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase genes downstream of the stress-induced ATF4-mediated transcription program. The anabolic response was associated with increased amino acid flux and charging of tRNAs for branched chain and aromatic amino acids (e.g. leucine and tryptophan), the levels of which are early serum indicators of diabetes. We conclude that regulation of amino acid transport in β-cells during ER stress involves responses leading to increased protein synthesis, which can be protective during acute stress but can lead to apoptosis during chronic stress. These studies suggest that the increased expression of amino acid transporters in islets can serve as early diagnostic biomarkers for the development of diabetes.
Keywords: Amino Acid Transport; Aminoacyl tRNA Synthetase; Beta Cell; Diabetes; ER Stress; Glutamine.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- DK15658/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK053307/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK060596/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK088227/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DK076174/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37-DK60596/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK015658/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK088227/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DK53307/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK042394/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37DK042394/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK048280/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DK76174/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK060596/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020572/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK48280/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

