Biopsy-proven drug-induced tubulointerstitial nephritis in a patient with acute kidney injury and alcoholic severe acute pancreatitis
- PMID: 23645698
- PMCID: PMC3669828
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2013-008557
Biopsy-proven drug-induced tubulointerstitial nephritis in a patient with acute kidney injury and alcoholic severe acute pancreatitis
Abstract
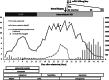
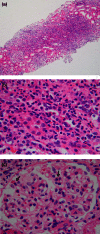
We report a 49-year-old man with alcoholic severe acute pancreatitis (SAP) complicated by drug-induced acute tubulointerstitial nephritis (DI-AIN). Oliguria persisted and became anuric again on day 17 despite improvement of pancreatitis. He presented rash, fever and eosinophilia from day 20. Renal biopsy was performed for dialysis-dependent acute kidney injury (AKI), DI-AIN was revealed, and prompt use of corticosteroids fully restored his renal function. This diagnosis might be missed because it is difficult to perform renal biopsy in such a clinical situation. If the patient's general condition allows, renal biopsy should be performed and reversible AKI must be distinguished from many cases of irreversible AKI complicated by SAP. This is the first report of biopsy-proven DI-AIN associated with SAP, suggesting the importance of biopsy for distinguishing DI-AIN in persisting AKI of SAP.
Figures
References
-
- Hao L, Zhaoxin Q, Zhiling L, et al. Risk factors and outcome of acute renal failure in patients with severe acute pancreatitis. J Crit Care 2010;2013:225–9 - PubMed
-
- Tran DD, Oe PL, Fijter CWH, et al. Acute renal failure in patients with acute pancreatitis: prevalence, risk factors, and outcome. Nephrol Dial Transplant 1993;2013:1079–84 - PubMed
-
- Imrie CW. Observations on acute pancreatitis. Br J Surg 1974;2013:539–44 - PubMed
-
- Alfonzo AV, Fox JG, Imrie CW, et al. Acute renal cortical necrosis in a series of young men with severe acute pancreatitis. Clin Nephrol 2006;2013:223–31 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
