Chromatin architecture, CCCTC-binding factor, and V(D)J recombination: managing long-distance relationships at antigen receptor loci
- PMID: 23645930
- PMCID: PMC3648861
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1300218
Chromatin architecture, CCCTC-binding factor, and V(D)J recombination: managing long-distance relationships at antigen receptor loci
Abstract
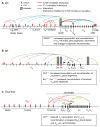
The rearrangement of T and B lymphocyte Ag receptor loci occurs within a highly complex chromosomal environment and is orchestrated through complex mechanisms. During the past decade, a large body of literature has highlighted the significance of chromatin architecture at Ag receptor loci in supporting the genomic assembly process: in preparation for recombination, these loci tend to contract and form multiple loops that shorten the distances between gene segments and facilitate recombination events. CCCTC-binding factor, CTCF, has received much attention in this regard since it has emerged as an important regulator of chromatin organization and transcription. In this review, we summarize recent work outlining conformational dynamics at Ag receptor loci during lymphocyte development and we discuss the role of CTCF in Ag receptor locus conformation and repertoire development.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Variable Extent of Lineage-Specificity and Developmental Stage-Specificity of Cohesin and CCCTC-Binding Factor Binding Within the Immunoglobulin and T Cell Receptor Loci.Front Immunol. 2018 Mar 8;9:425. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00425. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29593713 Free PMC article.
-
RAG Chromatin Scanning During V(D)J Recombination and Chromatin Loop Extrusion are Related Processes.Adv Immunol. 2018;139:93-135. doi: 10.1016/bs.ai.2018.07.001. Epub 2018 Aug 27. Adv Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30249335 Review.
-
An Ectopic CTCF Binding Element Inhibits Tcrd Rearrangement by Limiting Contact between Vδ and Dδ Gene Segments.J Immunol. 2016 Oct 15;197(8):3188-3197. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1601124. Epub 2016 Sep 9. J Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27613698 Free PMC article.
-
Tcra gene recombination is supported by a Tcra enhancer- and CTCF-dependent chromatin hub.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Dec 11;109(50):E3493-502. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1214131109. Epub 2012 Nov 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 23169622 Free PMC article.
-
Genome Topology Control of Antigen Receptor Gene Assembly.J Immunol. 2020 May 15;204(10):2617-2626. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1901356. J Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32366683 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Poor quality Vβ recombination signal sequences stochastically enforce TCRβ allelic exclusion.J Exp Med. 2020 Sep 7;217(9):e20200412. doi: 10.1084/jem.20200412. J Exp Med. 2020. PMID: 32526772 Free PMC article.
-
On the organization of human T-cell receptor loci: log-periodic distribution of T-cell receptor gene segments.J R Soc Interface. 2016 Jan;13(114):20150911. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2015.0911. J R Soc Interface. 2016. PMID: 26763333 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lineage-specific compaction of Tcrb requires a chromatin barrier to protect the function of a long-range tethering element.J Exp Med. 2015 Jan 12;212(1):107-20. doi: 10.1084/jem.20141479. Epub 2014 Dec 15. J Exp Med. 2015. PMID: 25512470 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay of Protein Binding Interactions, DNA Mechanics, and Entropy in DNA Looping Kinetics.Biophys J. 2015 Aug 4;109(3):618-29. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2015.06.054. Biophys J. 2015. PMID: 26244743 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of Topological Domains and Loop Formation to 3D Chromatin Organization.Genes (Basel). 2015 Jul 27;6(3):734-50. doi: 10.3390/genes6030734. Genes (Basel). 2015. PMID: 26226004 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Schatz DG, Swanson PC. V(D)J recombination: mechanisms of initiation. Annu Rev Genet. 2011;45:167–202. - PubMed
-
- Jung D, Giallourakis C, Mostoslavsky R, Alt FW. Mechanism and control of V(D)J recombination at the immunoglobulin heavy chain locus. Annu Rev Immunol. 2006;24:541–570. - PubMed
-
- Schatz DG, Ji Y. Recombination centres and the orchestration of V(D)J recombination. Nat Rev Immunol. 2011;11:251–263. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

