Chromatin architecture, CCCTC-binding factor, and V(D)J recombination: managing long-distance relationships at antigen receptor loci
- PMID: 23645930
- PMCID: PMC3648861
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1300218
Chromatin architecture, CCCTC-binding factor, and V(D)J recombination: managing long-distance relationships at antigen receptor loci
Abstract
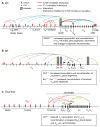
The rearrangement of T and B lymphocyte Ag receptor loci occurs within a highly complex chromosomal environment and is orchestrated through complex mechanisms. During the past decade, a large body of literature has highlighted the significance of chromatin architecture at Ag receptor loci in supporting the genomic assembly process: in preparation for recombination, these loci tend to contract and form multiple loops that shorten the distances between gene segments and facilitate recombination events. CCCTC-binding factor, CTCF, has received much attention in this regard since it has emerged as an important regulator of chromatin organization and transcription. In this review, we summarize recent work outlining conformational dynamics at Ag receptor loci during lymphocyte development and we discuss the role of CTCF in Ag receptor locus conformation and repertoire development.
Figures
References
-
- Schatz DG, Swanson PC. V(D)J recombination: mechanisms of initiation. Annu Rev Genet. 2011;45:167–202. - PubMed
-
- Jung D, Giallourakis C, Mostoslavsky R, Alt FW. Mechanism and control of V(D)J recombination at the immunoglobulin heavy chain locus. Annu Rev Immunol. 2006;24:541–570. - PubMed
-
- Schatz DG, Ji Y. Recombination centres and the orchestration of V(D)J recombination. Nat Rev Immunol. 2011;11:251–263. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

