Free fatty acid oxidation in insulin resistance and obesity
- PMID: 23646039
- PMCID: PMC3643515
Free fatty acid oxidation in insulin resistance and obesity
Abstract
The growing worldwide epidemic of obesity and diabetes portends a significant increase in cardiovascular disease. Obesity is associated with insulin resistance, and there is growing evidence that these conditions independently increase the risk of heart failure. Changes in myocardial substrate utilization develop in obesity and insulin resistance, and are characterized by increased fatty acid oxidation and utilization, and decreased glucose utilization. This paper will review the evidence for altered myocardial fatty acid utilization in obesity and insulin resistance, review mechanisms that are responsible, and discuss the relative contributions of systemic and myocardial insulin resistance in the regulation of fatty acid utilization in the heart.
Keywords: Fatty acid oxidation; insulin resistance; myocardial substrate utilization; obesity.
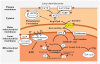
Figures

References
-
- Alberti KG, Eckel RH, Grundy SM, et al. Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome: a joint interim statement of the International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; American Heart Association; World Heart Federation; International Atherosclerosis Society; and International Association for the Study of Obesity. Circulation. 2009;120:1640–1645. - PubMed
-
- Boudina S, Abel ED. Diabetic cardiomyopathy revisited. Circulation. 2007;115:3213–3223. - PubMed
-
- Bugger H, Abel ED. Molecular mechanisms for myocardial mitochondrial dysfunction in the metabolic syndrome. Clin Sci (Lond) 2008;114:195–210. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
