Nuclear localization of the mitochondrial factor HIGD1A during metabolic stress
- PMID: 23646141
- PMCID: PMC3639984
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062758
Nuclear localization of the mitochondrial factor HIGD1A during metabolic stress
Abstract
Cellular stress responses are frequently governed by the subcellular localization of critical effector proteins. Apoptosis-inducing Factor (AIF) or Glyceraldehyde 3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase (GAPDH), for example, can translocate from mitochondria to the nucleus, where they modulate apoptotic death pathways. Hypoxia-inducible gene domain 1A (HIGD1A) is a mitochondrial protein regulated by Hypoxia-inducible Factor-1α (HIF1α). Here we show that while HIGD1A resides in mitochondria during physiological hypoxia, severe metabolic stress, such as glucose starvation coupled with hypoxia, in addition to DNA damage induced by etoposide, triggers its nuclear accumulation. We show that nuclear localization of HIGD1A overlaps with that of AIF, and is dependent on the presence of BAX and BAK. Furthermore, we show that AIF and HIGD1A physically interact. Additionally, we demonstrate that nuclear HIGD1A is a potential marker of metabolic stress in vivo, frequently observed in diverse pathological states such as myocardial infarction, hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE), and different types of cancer. In summary, we demonstrate a novel nuclear localization of HIGD1A that is commonly observed in human disease processes in vivo.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
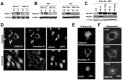
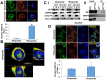
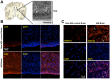


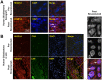
References
-
- Semenza GL, Agani F, Feldser D, Iyer N, Kotch L, et al. (2000) Hypoxia, HIF-1, and the pathophysiology of common human diseases. Adv Exp Med Biol 475: 123–130. - PubMed
-
- Takahashi E (2008) Anoxic cell core can promote necrotic cell death in cardiomyocytes at physiological extracellular PO2. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 294: H2507–2515. - PubMed
-
- Loor G, Schumacker PT (2008) Role of hypoxia-inducible factor in cell survival during myocardial ischemia-reperfusion. Cell Death Differ 15: 686–690. - PubMed
-
- Semenza GL (2011) Oxygen sensing, homeostasis, and disease. N Engl J Med 365: 537–547. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

