Enhanced endothelin receptor type B-mediated vasodilation and underlying [Ca²⁺]i in mesenteric microvessels of pregnant rats
- PMID: 23646960
- PMCID: PMC3831712
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.12225
Enhanced endothelin receptor type B-mediated vasodilation and underlying [Ca²⁺]i in mesenteric microvessels of pregnant rats
Abstract
Background and purpose: Normal pregnancy is associated with decreased vascular resistance and increased release of vasodilators. Endothelin-1 (ET-1) causes vasoconstriction via endothelin receptor type A (ET(A)R), but could activate ET(B)R in the endothelium and release vasodilator substances. However, the roles of ET(B)R in the regulation of vascular function during pregnancy and the vascular mediators involved are unclear.
Experimental approach: Pressurized mesenteric microvessels from pregnant and virgin Sprague-Dawley rats were loaded with fura-2/AM for simultaneous measurement of diameter and [Ca²⁺]i.
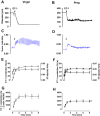
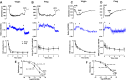
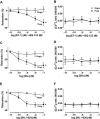
Key results: High KCl (51 mM) and phenylephrine (PHE) caused increases in vasoconstriction and [Ca²⁺]i that were similar in pregnant and virgin rats. ET-1 caused vasoconstriction that was less in pregnant than virgin rats, with small increases in [Ca²⁺]i. Pretreatment with the ET(B)R antagonist BQ-788 caused greater enhancement of ET-1-induced vasoconstriction in pregnant rats. ACh caused endothelium-dependent relaxation and decreased [Ca²⁺]i, and was more potent in pregnant than in virgin rats. ET-1 + ET(A)R antagonist BQ-123, and the ET(B)R agonists sarafotoxin 6c (S6c) and IRL-1620 caused greater vasodilation in pregnant than in virgin rats with no changes in [Ca²⁺]i, suggesting up-regulated ET(B)R-mediated relaxation pathways. ACh-, S6c- and IRL-1620-induced relaxation was reduced by the NO synthase inhibitor Nω-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester, and abolished by tetraethylammonium or endothelium removal. Western blots revealed greater amount of ET(B)R in intact microvessels of pregnant than virgin rats, but reduced levels in endothelium-denuded microvessels, supporting a role of endothelial ET(B)R.
Conclusions and implications: The enhanced ET(B)R-mediated microvascular relaxation may contribute to the decreased vasoconstriction and vascular resistance during pregnancy.
© 2013 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures




References
-
- Adner M, Geary GG, Edvinsson L. Appearance of contractile endothelin-B receptors in rat mesenteric arterial segments following organ culture. Acta Physiol Scand. 1998a;163:121–129. - PubMed
-
- Adner M, Uddman E, Cardell LO, Edvinsson L. Regional variation in appearance of vascular contractile endothelin-B receptors following organ culture. Cardiovasc Res. 1998b;37:254–262. - PubMed
-
- Alexander BT, Rinewalt AN, Cockrell KL, Massey MB, Bennett WA, Granger JP. Endothelin type a receptor blockade attenuates the hypertension in response to chronic reductions in uterine perfusion pressure. Hypertension. 2001;37:485–489. - PubMed
-
- Anderson CM, Lopez F, Zhang H-Y, Shirasawa Y, Pavlish K, Benoit JN. Mestenteric vascular responsiveness in a rat model of pregnancy-induced hypertension. Exp Biol Med. 2006a;231:1398–1402. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

