Activation of adenosine A(2A) receptor reduces osteoclast formation via PKA- and ERK1/2-mediated suppression of NFκB nuclear translocation
- PMID: 23647065
- PMCID: PMC3831714
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.12227
Activation of adenosine A(2A) receptor reduces osteoclast formation via PKA- and ERK1/2-mediated suppression of NFκB nuclear translocation
Abstract
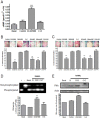
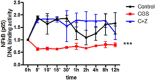
Background and purpose: We previously reported that adenosine, acting at adenosine A(2A) receptors (A(2A)R), inhibits osteoclast (OC) differentiation in vitro (A(2A)R activation OC formation reduces by half) and in vivo. For a better understanding how adenosine A(2A)R stimulation regulates OC differentiation, we dissected the signalling pathways involved in A(2A)R signalling.
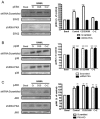
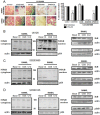
Experimental approach: OC differentiation was studied as TRAP+ multinucleated cells following M-CSF/RANKL stimulation of either primary murine bone marrow cells or the murine macrophage line, RAW264.7, in presence/absence of the A(2A)R agonist CGS21680, the A(2A)R antagonist ZM241385, PKA activators (8-Cl-cAMP 100 nM, 6-Bnz-cAMP) and the PKA inhibitor (PKI). cAMP was quantitated by EIA and PKA activity assays were carried out. Signalling events were studied in PKA knockdown (lentiviral shRNA for PKA) RAW264.7 cells (scrambled shRNA as control). OC marker expression was studied by RT-PCR.
Key results: A(2A)R stimulation increased cAMP and PKA activity which and were reversed by addition of ZM241385. The direct PKA stimuli 8-Cl-cAMP and 6-Bnz-cAMP inhibited OC maturation whereas PKI increased OC differentiation. A(2A)R stimulation inhibited p50/p105 NFκB nuclear translocation in control but not in PKA KO cells. A(2A)R stimulation activated ERK1/2 by a PKA-dependent mechanism, an effect reversed by ZM241385, but not p38 and JNK activation. A(2A)R stimulation inhibited OC expression of differentiation markers by a PKA-mechanism.
Conclusions and implications: A(2A)R activation inhibits OC differentiation and regulates bone turnover via PKA-dependent inhibition of NFκB nuclear translocation, suggesting a mechanism by which adenosine could target bone destruction in inflammatory diseases like rheumatoid arthritis.
© 2013 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures


References
-
- Blair HC, Robinson LJ, Zaidi M. Osteoclast signalling pathways. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;328:728–738. - PubMed
-
- Bohm C, Hayer S, Kilian A, Zaiss MM, Finger S, Hess A, et al. The alpha-isoform of p38 MAPK specifically regulates arthritic bone loss. J Immunol. 2009;183:5938–5947. - PubMed
-
- van Calker D, Muller M, Hamprecht B. Adenosine regulates via two different types of receptors, the accumulation of cyclic AMP in cultured brain cells. J Neurochem. 1979;33:999–1005. - PubMed
-
- Chan ES, Cronstein BN. Methotrexate – how does it really work? Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2010;6:175–178. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

