Impaired vascular KATP function attenuates exercise capacity in obese zucker rats
- PMID: 23647569
- PMCID: PMC3778059
- DOI: 10.1111/micc.12065
Impaired vascular KATP function attenuates exercise capacity in obese zucker rats
Abstract
Objective: Obese subjects exhibit decreased exercise capacity (VO2max ). We have shown that vascular KATP channel mediates arteriolar dilation to muscle contraction. We hypothesize that exercise capacity is decreased in obesity due to impaired vascular KATP function.
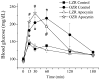
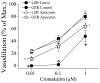
Methods: The VO2max was measured in LZR and OZR by treadmill running before and following treatment with the KATP blocker glibenclamide i.p. One week later, the spinotrapezius muscle was prepared for in vivo microscopy. Arcade arteriolar diameters were measured following muscle contraction or application of the KATP opener cromakalim before and after glibenclamide application. In additional animals, LZR and OZR were treated with apocynin for five weeks. VO2max and arteriolar dilation experiments were repeated.
Results: The OZR exhibited decreased VO2max , functional and cromakalim-induced vasodilation as compared with LZR. Glibenclamide had no effect on VO2max and functional vasodilation in OZR, but significantly inhibited responses in LZR. Vascular superoxide levels and NADPH oxidase activity were increased in OZR, but reduced in apocynin-treated OZR. Apocynin increased the VO2max , functional and cromakalim-induced vasodilation in OZR with no effect in LZR.
Conclusions: Exercise capacity is dependent on vascular KATP channel function. The reduced exercise capacity in OZR appears to be due in part to superoxide-mediated impairment in vascular KATP function.
Keywords: KATP channels; NADPH oxidase; obese; superoxide; vascular.
© 2013 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures




References
-
- Bäumer AT, Krüger CA, Falkenberg J, Freyhaus HT, Rösen R, Fink K, Rosenkranz S. The NAD(P)H oxidase inhibitor apocynin improves endothelial NO/superoxide balance and lowers effectively blood pressure in spontaneously hypertensive rats: comparison to calcium channel blockade. Clin Exp Hypertens. 2007;29(5):287–99. - PubMed
-
- Bank AJ, Sih R, Mullen K, Osayamwen M, Lee PC. Vascular ATP-dependent potassium channels, nitric oxide, and human forearm reactive hyperemia. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2000;14(1):23–9. - PubMed
-
- Chen Y, Traverse JH, Zhang J, Bache RJ. Selective blockade of mitochondrial KATP channels does not impair myocardial oxygen consumption. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2001;281(2 50-2):H738–H744. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

