A novel quinoline derivative that inhibits mycobacterial FtsZ
- PMID: 23647650
- PMCID: PMC3686551
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tube.2013.04.002
A novel quinoline derivative that inhibits mycobacterial FtsZ
Abstract
High throughput phenotypic screening of large commercially available libraries through two NIH programs has produced thousands of potentially interesting hits for further development as antitubercular agents. Unfortunately, these screens do not supply target information, and further follow up target identification is required to allow optimal rational design and development of highly active and selective clinical candidates. Cheminformatic analysis of the quinoline and quinazoline hits from these HTS screens suggested a hypothesis that certain compounds in these two classes may target the mycobacterial tubulin homolog, FtsZ. In this brief communication, activity of a lead quinoline against the target FtsZ from Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) is confirmed as well as good in vitro whole cell antibacterial activity against Mtb H37Rv. The identification of a putative target of this highly tractable pharmacophore should help medicinal chemists interested in targeting FtsZ and cell division develop a rational design program to optimize this activity toward a novel drug candidate.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures

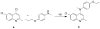
References
-
- Koul A, Arnoult E, Lounis N, Guillemont J, Andries K. The challenge of new drug discovery for tuberculosis. Nature. 2011;469:483–90. - PubMed
-
- Ananthan S, Faaleolea ER, Goldman RC, Hobrath JV, Kwong CD, Laughon BE, Maddry JA, Mehta A, Rasmussen L, Reynolds RC, Secrist JA, III, Shindo N, Showe DN, Sosa MI, Suling WJ, White EL. High-throughput screening for inhibitors of Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv. Tuberculosis (Edinb) 2009;89:334–53. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Reynolds RC, Ananthan S, Faaleolea E, Hobrath JV, Kwong CD, Maddox C, Rasmussen L, Sosa MI, Thammasuvimol E, White EL, Zhang W, Secrist JA., III High throughput screening of a library based on kinase inhibitor scaffolds against Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv. Tuberculosis (Edinb) 2012;92:72–83. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

